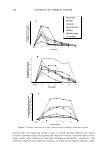
412 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE A FAMILY OF EMOLLIENT ESTERS EXHIBITS ANTI-MICROBIAL PROPERTIES OF PRACTICAL USE TO FORMULATORS SEEKING TO REDUCE OR ELIMINATE THE USE OF PRESERVATIVES Introduction Monna Manning and Philip Orawski Abitec Corporation, Columbus, OH Kabara and others found that certain fatty acids and esters were useful as antimicrobial agents. 1• 2· 3 Based upon these findings, high purity monoesters of glycerin or propylene glycol were synthesized and assayed for their efficacy against traditional preservatives. Three emollient esters were selected for their anti-microbial properties. This range of high purity short-chain monoglyceride esters have been shown to offer performance comparable to "conventional" anti microbial agents or preservatives, without the need to register as preservatives. Experimental MIC Test and selection of three monoglycerides Eleven (11) structures were evaluated in a Minimum Inhibitory Concentration test (USP 61 "Microbial Limit Tests"), which tests the efficacy of antimicrobial agents versus concentration. Based upon performance in this test, three structures were chosen to pursue as commercially viable products. In all, eleven (11) organisms were used in MIC testing. The following tables indicate the results for four (4) of the most common organisms: Candida albicans ( a yeast), Aspergillus niger (a mold), Staphylococcus aureus (a gram positive bacterium), and Eschirichia. coli (a gram negative bacterium). The legend is"+" to indicate growth, and"-" to indicate microbiological kill. % Dilution 0.010 0.025 0.050 0.075 0.100 0.175 0.250 0.500 0.750 1.000 Candida albicans Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + + Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + Glyceryl Caprylate + + + Aspergillus niger Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + Glyceryl Caprylate + + + + + Staphylococcus aureus Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + + + + Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + + Glyceryl Caprylate + + + Escherichia coli Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + + + + Propylene Glycol Heptanoat + + + + + + + + + + Glyceryl Caprylate + + + + + + + Challenge Test comparison to DMDM Hydantoin and parabens
2004 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR 413 In a typical TEA Stearate Lotion formulation, three anti-microbial monoglycerides were evaluated in a challenge test (USP 51 "Antimicrobial Effectiveness Testing") against a blend of 0.2% Methylparaben and 0.1 % Propylparaben or against 0.4% DMDM Hydantoin. The individual esters were tested at 0.5%, which is the recommended minimum usage level. E. coli S. aureus A. niger C. albicans Propylene ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Glycol Heptanoate Outperformed Outperformed parabens Zero Growth. Outperformed @0.5%in Parabens@ @ 0.3% or DMDM Equal to O .3 % 0.4%DMDM lotion 0.3% Hydantoin@0.4% parabens or DMDM Hydantoin Hydantoin@0.4% Propylene ✓ ✓ Glycol Caprylate Outperformed Outperformed Parabens Performance Performance @0.5%in Parabens@ @0.3% marginally inferior marginally lotion 0.3% inferior Glycerol ✓ ✓ ✓ ✓ Caprylate @0.5 %in lotion Outperformed Outperformed 0.3% Zero Growth. Outperformed 0 .3 % parabens parabens or 0.4% Equal to 0.3% 0.4%DMDM DMDM Hydantoin parabens or O .4% Hydantoin DMDM Hyclantoin Discussion Additional MIC and Challenge test data will be presented and results and implications discussed. References 1. US Pat 4,002,775 Fatty acids and Derivatives of Antimicrobial Agents, Jon Kabara, (January 11, 1977) 2. A Branan and P Davison, Anti-microbials in Foods, Marcel Dekker, ed., New York, ( 1986) pp 109-140 3. J Kabara, and M Ohkawa, et al., Examination on Antitumor, Immunological, and Plant Growth Inhibitory Effects on Monoglycerides of Caprylic Capric and Laurie Acids and Related Compounds Pharmacological Effects of Lipids, Volume II, (1985) pp 263-272
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)