416 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Formula C. Water-in-Oil Emulsion Formulation •Cyclomethicone and Dimethicone Copolyol •Cyclomethicone •Cyclomethicone and Dimethicone •Methyl Glucose Dioleate • Dimethicone Copolyol •Brassica Campestris / Aleurites Fordii Oil Copolymer •C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate • Lanolin Alcohol •Water •Sodium Chloride •Titanium Dioxide (+Coatings) 5.0-10.0% Four distinct dispersions were made and evaluated. See Table 1 below. DISPERSION ( 1 ) C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate Titanium Dioxide (10 nm) ( and ) aluminum hydroxide ( and ) stearic acid Lecithin Polyglyceryl 3- Diisostearate Cetyl Dimethicone Copolyol DISPERSION ( 2 ) C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate Titanium Dioxide (15 nm) ( and ) aluminum hydroxide ( and ) stearic acid Lecithin Polyglyceryl 3-Diisostearate Cetyl Dimethicone Copolyol DISPERSION ( 3 ) PEG-7 Methyl Ether Titanium Dioxide (20 nm) ( and ) glycerin ( and ) alumina Mono-and dibutyl phosphate Table 1. Dispersion compositions by INCi name designations. In vitro sunscreen analysis: •Optometries 290 In vitro SPF analyzer (Optometries, Ayer, MA, USA) DISPERSION ( 4 ) C12-15 Alkyl Benzoate Titanium Dioxide (21 nm) (and) Trimethoxycaprylylsilane Polyglyceryl 3-Diisostearate Lecithin Cetyl Dimethicone Copolyol •Vitro Skin™ - IMS (Innovative Measurement Systems, CT, USA) VITRO-SKIN TM is an advanced testing substrate that effectively mimics the surface properties of human skin. It contains both optimized protein and lipid components and is designed to have topography, pH, critical surface tension and ionic strength similar to human skin. 2 µLI cm2 product application per FDA OTC Monograph. Each sample result is the average of twelve (12) runs made at preset positions on the X-Y stage of the SPF Analyzer. In vivo sunscreen analysis: SPF: FDA Protocol per OTC Final Monograph: 64 Fed. Reg. 27666 May 21,1999: Twenty (n=20) subjects of skin types 1--Always bums easily never tans (sensitive). II-Always bums easily tans minimally (sensitive). 111--Bums moderately tans gradually (light brown) (normal). 2µL/ cm2 application
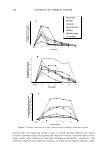
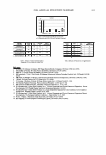
2004 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR 417 dosage. Calculate SPF value= the ratio of erythema effective exposure for protected skin (Joules per square meter) (MED (PS)) to the erythema effective exposure for unprotected skin (Joules per square meter) (MED (US)) per the Final Monograph. UV A: JClA protocol PPD (persistent pigment darkening): Ten (n=lO) subjects of skin types II, III, and/or IV. 2@U cm2 application dosage. Irradiation with UV A (320-400 nm) by filtered solar simulator radiation with ratio of UV A I (340- 400) to UV A II (320-340 nm) close to that of natural sunlight. UV A Protection Factor (PFA) calculated as ratio of the minimal persistent pigment darkening dose (read at 2-4 hours) required to elicit dar ·ening a1 the product treated site versus the untreated site. Results: Smaller particle size generally yields higher SPF efficacy" but with less UV A absorption herice lower critical wavelength at lower particle size. See Table 2 below Particle size / 10nm 15 nm 20nm 21 nm 35 nm 180nm 1000 nm Properties .. . -- "'i-• ..._,.......-,i . ' •• �•• .. I SPF/%TI02 2.19 2.3 0.91 1.83 1.44 0.76 NIA Critical lambda 369.4 374 382.4 375.35 331.6 384.15 NIA UVA/UVB 0.419 0.509 0.752 0.533 0.726 0.811 NIA - 'R\ SPF/% Tl02 1.64 NIA 2.03 71.42 NIA NIA NIA Critical Lambda 370.85 NIA 379.45 374.7 NIA NIA NIA UVA/UVB 0.422 NIA 0.662 0.491 NIA NIA NIA ��I•-··. :·:"¥f-Jfflll SPF/%TI02 2.34 1.89 3.56 1.73 NIA NIA 0.37 Critical Lambda 367.35 373 380 376.6 NIA NIA 385.25 UVA/ UVB 0.394 0.494 0.701 0.546 NIA NIA 0.652 - Table 2. Particle size of Titanium Dioxides and sunscreen performance 11ro ,erties In comparing results with powders used as is and dispersed during processing of che emulsion, equivalent dispersions formulated and made prior to batch preparation give higher SPF values and slightly lower critical wavelengths. This would s ggest better dispersion in the skin film with higher UVB attenuation and better transparency. Draw down films demonstrate the increase transparency. Some anomalous results suggest that the disper ·ions are not optimized for that type emulsion and do not promote even distribmion in the skin film. Creams made with optimized liquid crystalline lamellar gel networks seem to � shifted out of balance when either the combination of dispersing agents interacts wit the gel network or the surf ace area of the inorganic sunscreen adsorbs hydrophilic surfactant from the ge] networ ·. See Table 3 below. TI02 s powder vs Dispersion TI02 ( 1 ) Dtaperston TI02 ( 2) DI pe Ion Tl02 ( 3) Dispersion TIO ( ) Dlsperalon (1) (2) (3) (4)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)