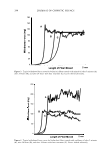
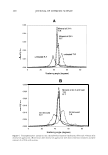
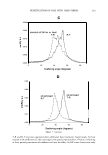
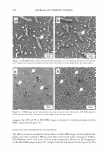
CATIONIC CONDITIONING COMPOUNDS 325 conditioner-treated hair fibers were cross-sectioned each time with a clean stainless steel blade and mounted in small holders with the cross sections facing the spectrometer at a slight tilt. ION MASS SPECTRA Ion mass spectra were collected to isolate characteristic positive/negative ions of the cationics. Positive and negative static TOF SIMS spectra were acquired from several locations on each of the cationic conditioning compounds and from the surface of the hair-fiber cross section. The sampling depth of TOF SIMS is only -1 monolayer for molecular fragment ions and one to three monolayers for atomic species. Since the sampling depth of TOF SIMS is only approximately one molecular layer, only the low-molecular-weight, highly mobile, components in the surface are detected. The higher-molecular-weight compounds are more difficult, if not impossible, to ionize with the 69 Ga + liquid metal ion gun. Therefore, one has to look at the low-molecular weight fragments of the high-molecular-weight compounds. Detecting the fragments, in turn, is indicative of the presence of high-molecular-weight compounds. Positive and negative mass spectra are plotted as the number of secondary ions detected (y-axis, counts) versus the mass-to-charge ratio of the ions (x-axis, m/z). IMAGING Imaging/mapping the presence of cationics within the fiber cross section. Once the characteristic or unique positive or negative ions (atomic species or low-molecular-weight fractions) of the conditioning compounds were established, their diffusion into the fiber cross section was mapped. RES UL TS AND DISCUSSION CHARACTERISTIC POSITIVE AND NEGATIVE IONS OF CET AB Characteristic positive ions of CETAB are C 3 H 8 N + at 58 m/z, (CH 2 \NH 2 + at 114, 128, 142, 156, 170, 184, and 198 m/z, and C 19 H4 2 N + at 284.33 m/z. Although mass C 3 H 8 N+ at 58 m/z is relatively intense, it is probably not a good ion for imaging, since it can be formed from a wide variety of amines and may, therefore, not necessarily be indicative of CETAB if other amines exist. The positive ion C1 9 H4 2 N + at 284.33 m/z is the best ion and will be used for imaging, since it is intense and is likely to be free of mass interference. In combination with this latter ion, imaging of C 3 H 8 N + at 58 m/z will support the presence of CETAB as well. 79 Br- and 81 Br - are characteristic negative ions of CET AB. Because the organic portion of CETAB forms strong positive ions, it tends to form weak negative ions. However, since the presence of sulfates also produces a peak at 81 m/z due to HSO 3 - , that peak is not ideal for mapping CETAB. Therefore, the negative 79 Br- ion seems to be the best for imaging CETAB through the negative ions.
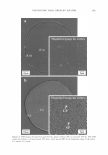
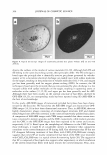
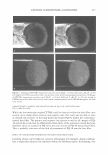
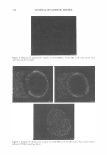
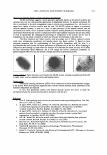
326 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE IMAGING CETAB'S CHARACTERISTIC POSITIVE IONS IN UNTREATED HAIR FIBERS (CONTROLS) To establish the presence of CET AB in the cross section of CETAB-treated hair fibers, the positive ions of C 3 H 8 N + at 58 m/z and C 19 H 42 N + at 284 m/z were imaged first in untreated hair fibers and will serve as reference images for comparison (Figure 1). The images in Figure 1 do not show any CETAB activity within the untreated hair fiber. IMAGING CETAB'S CHARACTERISTIC POSITIVE IONS IN CETAB-TREATED HAIR FIBERS In contrast to the control fibers, images of CETAB-treated hair fibers at mass numbers 58 and 284 (Figure 2a,b) clearly show that CETAB has penetrated into the fiber interior. The extent of penetration, however, varies from fiber to fiber. In some cases, the CET AB penetration is restricted to the fiber periphery (broad ring) (Figure 2a), while other fibers have been penetrated uniformly throughout the bulk of the hair-fiber (Figure 26). These differences in penetration and the amount of CETAB may be due to differences in fiber history and constitution. It is important to note that the similarity of images at the two different mass numbers, 58 and 284, in Figure 2a,b support the idea that these two ions come from fragments of CET AB. IMAGING CETAB'S CHARACTERISTIC NEGATIVE IONS IN THE CROSS SECTION OF UNTREATED HAIR FIBERS The negative ion image of CETAB at 79 m/z (Br-) in an untreated control hair fiber is shown in Figure 3. The 79 Br- image in untreated hair does not show much activity. IMAGING CETAB'S CHARACTERISTIC NEGATIVE IONS IN THE CROSS SECTION OF CETAB-TREATED HAIR FIBERS The 79 Br- ion image of the CETAB-treated hair fiber (Figure 4) once again shows partial to complete penetration of CETAB into the bulk of the hair fiber, as was observed in the positive ion imaging. Figure 1. Imaging the presence of two of the characteristic positive ions of CET AB (left: C3H8N+ at 58 m/z right: C 19 H42N + at 284 m/z) in the surface of the cross section of an untreated hair fiber (serving as control).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)