16
5 e
L 4
T 3
CQ.
� 2
(/)
G) C: �
-�
t- a
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
(A) E-layer
NS NS ******
None MeOH Ace Hex Cl/Me
18 e
-5 17
L � 16
.!!!
I 15
'O ....,14 0
gi 13
i 12 1
11
I-
10
(B) � -layer
***
None MeOH Ace
NS
Hex Cl/Me
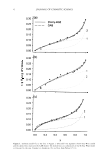
Figure 4. Effects of extraction with solvents on the thickness of the 13- and S-layers. (A) 13-layer. (B) S-layer.
None: non-extracted. MeOH: extracted with methanol. Ace: extracted with acetone. Hex: extracted with
hexane. Cl/Me: extracted with a mixture of chloroform and methanol (2:1). Mean± standard derivation (four
hair lots, each n =7). Statistical significance was analyzed using a Dannett test. NSP 0.05, ***p 0.001.
4.0 e
s
3.6 -
T 3.2 �
CQ.
'15
(/)2.8 �
..ll:: 2.4 (,)
-
2.0
40
(A) 8-Iayer
• •
• •
R2=0.1153
(p0.05)
''
41 42 43
Dyeing extent (A. E)
(B) 5 -layer
16.5
-
E ..s
16.0 •
15.5 T
'O
'+-15.0
14.5
4) C R2=0.8569
•
�
(,)14.0 :c (p0.05)
I-
13.5
44 40 41 42 43 44
Dyeing extent (AE)
Figure 5. Relationships between the CMC structure and the extent of dyeing. (A) Relationship between the
thickness of the 13-layer and the extent of dyeing. (B) Relationship between the thickness of the S-layer and
the extent of dyeing.
hydrophilic characteristics, demonstrated a strong effect on the 8-layer (protein layer),
whereas hexane, which has hydrophobic characteristics, primarily had an effect on the
�-layer (lipid layer). In addition, acetone, with an intermediate hydrophobicity between
methanol and hexane, had effects on both the 0- and �-layers, while the effect of the
mixture of chloroform/ methanol was similar to that of methanol.
Our results showed that extraction with solvent of elevated the extent of dyeing in
human hair. It was previously reported that solvent extraction accelerated the dyeing rate
of wool fiber (9). The differences in the extent of dyeing seen in the present study with
the different solvents were apparently related to the changes in the dyeing rate rather
than changes in dye-binding capacity. The dyeing period used (five minutes) was rela-
5 e
L 4
T 3
CQ.
� 2
(/)
G) C: �
-�
t- a
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
(A) E-layer
NS NS ******
None MeOH Ace Hex Cl/Me
18 e
-5 17
L � 16
.!!!
I 15
'O ....,14 0
gi 13
i 12 1
11
I-
10
(B) � -layer
***
None MeOH Ace
NS
Hex Cl/Me
Figure 4. Effects of extraction with solvents on the thickness of the 13- and S-layers. (A) 13-layer. (B) S-layer.
None: non-extracted. MeOH: extracted with methanol. Ace: extracted with acetone. Hex: extracted with
hexane. Cl/Me: extracted with a mixture of chloroform and methanol (2:1). Mean± standard derivation (four
hair lots, each n =7). Statistical significance was analyzed using a Dannett test. NSP 0.05, ***p 0.001.
4.0 e
s
3.6 -
T 3.2 �
CQ.
'15
(/)2.8 �
..ll:: 2.4 (,)
-
2.0
40
(A) 8-Iayer
• •
• •
R2=0.1153
(p0.05)
''
41 42 43
Dyeing extent (A. E)
(B) 5 -layer
16.5
-
E ..s
16.0 •
15.5 T
'O
'+-15.0
14.5
4) C R2=0.8569
•
�
(,)14.0 :c (p0.05)
I-
13.5
44 40 41 42 43 44
Dyeing extent (AE)
Figure 5. Relationships between the CMC structure and the extent of dyeing. (A) Relationship between the
thickness of the 13-layer and the extent of dyeing. (B) Relationship between the thickness of the S-layer and
the extent of dyeing.
hydrophilic characteristics, demonstrated a strong effect on the 8-layer (protein layer),
whereas hexane, which has hydrophobic characteristics, primarily had an effect on the
�-layer (lipid layer). In addition, acetone, with an intermediate hydrophobicity between
methanol and hexane, had effects on both the 0- and �-layers, while the effect of the
mixture of chloroform/ methanol was similar to that of methanol.
Our results showed that extraction with solvent of elevated the extent of dyeing in
human hair. It was previously reported that solvent extraction accelerated the dyeing rate
of wool fiber (9). The differences in the extent of dyeing seen in the present study with
the different solvents were apparently related to the changes in the dyeing rate rather
than changes in dye-binding capacity. The dyeing period used (five minutes) was rela-