48 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
stability of formulations (7). Magnesium aluminum silicate, which was added to the F2
formulation, is widely used as a thickening agent in many cosmetic preparations, due to
its thixotropic and pseudoplastic properties. The colloidal structure of this clay provides
excellent suspension of fine particles in aqueous systems (16) however, it did not offer
the suspension efficiency of other clay particles (kaolin and montmorillonite) in the
formulations studied.
Clays and organic thickeners, such as gums, are often used synergistically in cosmetic
products to provide a balance of suspension stability. The gums' protective colloidal
action improves clay stability in the presence of electrolytes, surfactants, water-solubles,
and even against phase separation (11,17). This fact was also observed in this study, once
hydroxypropyl starch phosphate (Fl) and xantham (F3) gums promoted stability in both
formulations after centrifuge testing, preventing phase separation. Therefore, only the
Fl and F3 formulations were classified as normal after PST, and they were submitted to
AST.
ACCELERATED ST ABILITY TEST (AST)
Formulations Fl and F3 maintained normal color and odor in all storage conditions.
These formulations did not present variation in the initial pH value (7 .3), superior to
± 1.0%, probably due to the buffer effect of clay that occurs when a suspension is at a pH
very near its natural pH (range of pH close to 6.0 or 7.5-8.0) (18). However, they
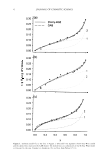
presented variations in visual aspect (Table I) and apparent viscosity (Figure 1) in the
same evaluated conditions. These alterations could be associated with temperature and
time influences on the clay hydration process.
The structural framework of clay is composed of thousands of submicroscopic platelets
Table I
Visual Aspects Observed in Fl and F3 Formulations at Different Temperatures in Storage Conditions in
the Accelerated Stability Test
Temperatures of
storage conditions
5.0° ± 0.5°C
22° ± 2.0°C
45.0° ± 0.5°C
-10.0° ± 0.5°C/24 h
45.0° ± 0.5°C/24 h
Days of
analysis
t
l 3
7
14
3
7
14
3
7
14
7
14
t
1 =24 h after preparation of clay masks.
SM =slightly modified.
N =normal.
Visual aspect
Fl F3
Homogeneous Homogeneous
SM SM
SM SM
SM SM
N SM
N SM
N SM
SM SM
SM SM
SM N
SM N
SM N
stability of formulations (7). Magnesium aluminum silicate, which was added to the F2
formulation, is widely used as a thickening agent in many cosmetic preparations, due to
its thixotropic and pseudoplastic properties. The colloidal structure of this clay provides
excellent suspension of fine particles in aqueous systems (16) however, it did not offer
the suspension efficiency of other clay particles (kaolin and montmorillonite) in the
formulations studied.
Clays and organic thickeners, such as gums, are often used synergistically in cosmetic
products to provide a balance of suspension stability. The gums' protective colloidal
action improves clay stability in the presence of electrolytes, surfactants, water-solubles,
and even against phase separation (11,17). This fact was also observed in this study, once
hydroxypropyl starch phosphate (Fl) and xantham (F3) gums promoted stability in both
formulations after centrifuge testing, preventing phase separation. Therefore, only the
Fl and F3 formulations were classified as normal after PST, and they were submitted to
AST.
ACCELERATED ST ABILITY TEST (AST)
Formulations Fl and F3 maintained normal color and odor in all storage conditions.
These formulations did not present variation in the initial pH value (7 .3), superior to
± 1.0%, probably due to the buffer effect of clay that occurs when a suspension is at a pH
very near its natural pH (range of pH close to 6.0 or 7.5-8.0) (18). However, they
presented variations in visual aspect (Table I) and apparent viscosity (Figure 1) in the
same evaluated conditions. These alterations could be associated with temperature and
time influences on the clay hydration process.
The structural framework of clay is composed of thousands of submicroscopic platelets
Table I
Visual Aspects Observed in Fl and F3 Formulations at Different Temperatures in Storage Conditions in
the Accelerated Stability Test
Temperatures of
storage conditions
5.0° ± 0.5°C
22° ± 2.0°C
45.0° ± 0.5°C
-10.0° ± 0.5°C/24 h
45.0° ± 0.5°C/24 h
Days of
analysis
t
l 3
7
14
3
7
14
3
7
14
7
14
t
1 =24 h after preparation of clay masks.
SM =slightly modified.
N =normal.
Visual aspect
Fl F3
Homogeneous Homogeneous
SM SM
SM SM
SM SM
N SM
N SM
N SM
SM SM
SM SM
SM N
SM N
SM N