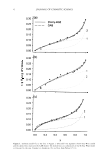
THE HUMAN NAIL: SORPTION ISOTHERMS 9
cysteine or 2-mercaptoethanol on the in vitro permeation of 5-fluorouracil or tolnaftate through the
human nail plate, Chern. Pharrn. Bull., 46, 1797-1802 (1998).
(15) G. Gupchup-Malhotra and J. Zatz, Investigation of nail permeation enhancement by chemical modi-
fication using water as a probe,]. Phann. Sci., 91, 312-323 (2002).
(16) X. Hui, T. C. Chan, S. Barbadillo, C. Lee, H. I. Maibach, and R. C. Wester. Enhanced econazole
penetration into human nail by 2-n-nonyl-1, 3-dioxolane,J. Pharrn. Sci., 92, 142-148 (2003).
(17) H. Baden, The physical properties of nail,]. Invest. Derrnatol., 55, 115-122 (1970).
(18) R. A. Robinson and R.H. Stokes, Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd ed. (Butterworths, London, 1970).
(19) H.B. Gunt, Effect of Hydration on Hurnan Nail Permeability, Ph.D. thesis, College of Pharmacy,
University of Cincinnati, August 2006.
(20) A. Adamson, Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 3rd ed (John Wiley &Sons, New York, 1976), pp.
565-570.
(21) G. B. Kasting and N. D. Barai. Equilibrium water sorption in human stratum corneum,j. Pharrn. Sci.,
92, 1624-1631 (2003).
(22) G. Zografi, M. J. Kontny, A. Y. Yang, and G. S. Brenner, Surface area and water vapor sorption of
microcrystalline cellulose, Int. J. Pharrn., 18, 99-116 (1984).
(23) A. Jonquieres and A. Fane, Modified BET models for modeling water vapor sorption in hydrophilic
glassy polymers and systems deviating strongly from ideality, J. Appl. Polymer Sci, 67, 1415-1430
(1998).
(24) P. Lewicki, The applicability of the GAB model to food water sorption isotherms, Int.]. Food Sci. Tech.,
32, 553-557 (1997).
(25) M. M. Pradas, M. S. Sanchez, G. G. Ferrer, and J. L. Ribelles, Thermodynamics and statistical me-
chanics of multilayer adsorption,]. Chern. Phys., 121, 8524-8531 (2004).
(26) A. F. El-Shimi, and H. M. Princen, Water vapor sorption and desorption behavior of some keratins,
Colloid Polymer Sci., 256, 105-114 (1978).
(27) K. Walkley, bound water in stratum corneum measured by differential scanning calorimetry,]. Invest.
Derrnatol., 59, 225-227 (1972).
(28) B. Turek, M. Vieu, M. Leduc, I. Nadvornik, and E. Jedia, Water content and moisture-binding
capacity of some types of human soft and hard horn, Curr. Med. Res. Opin., 7, 87-90 (1982).
(29) A. Adamson, Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 3rd ed. (John Wiley &Sons, New York, 1976), pp.
582-585.
(30) T. Yabuza, Creation of moisture sorption isotherms for hygroscopic materials, http://faculty
.che.urnn.edu!fscn!Ted_Labuza/PDF Jiles/Papers!Creation_Moistzm_jsotherrns.PDF, accessed 7 /3/06.
(31) C. Robbins, "The Physical Properties and Cosmetic Behavior of Hair," in Chemical and Physical Behavior
of Hurnan Hair, 3rd ed. (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1994), pp. 299-370.
(32) S. Wessel, M. Gniadecka, G. Jemec, and H. Wulf, Hydration of human nails investigated by NIR-
FT-Raman spectroscopy, Biochirn. Biophys. Acta, 1433, 210-216 (1999).
(33) C. W. Vertucci and A. C. Leopold, The relationship between water binding and desiccation tolerance
in tissues, Plant Physiol., 85, 232-238 (1987).
(34) F. J. Wortmann, P. Augustin, and C. Popescu, Temperature dependence of the water-sorption iso-
therms of wool,]. Appl. Polymer Sci., 79, 1054-1061 (2001).
cysteine or 2-mercaptoethanol on the in vitro permeation of 5-fluorouracil or tolnaftate through the
human nail plate, Chern. Pharrn. Bull., 46, 1797-1802 (1998).
(15) G. Gupchup-Malhotra and J. Zatz, Investigation of nail permeation enhancement by chemical modi-
fication using water as a probe,]. Phann. Sci., 91, 312-323 (2002).
(16) X. Hui, T. C. Chan, S. Barbadillo, C. Lee, H. I. Maibach, and R. C. Wester. Enhanced econazole
penetration into human nail by 2-n-nonyl-1, 3-dioxolane,J. Pharrn. Sci., 92, 142-148 (2003).
(17) H. Baden, The physical properties of nail,]. Invest. Derrnatol., 55, 115-122 (1970).
(18) R. A. Robinson and R.H. Stokes, Electrolyte Solutions, 2nd ed. (Butterworths, London, 1970).
(19) H.B. Gunt, Effect of Hydration on Hurnan Nail Permeability, Ph.D. thesis, College of Pharmacy,
University of Cincinnati, August 2006.
(20) A. Adamson, Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 3rd ed (John Wiley &Sons, New York, 1976), pp.
565-570.
(21) G. B. Kasting and N. D. Barai. Equilibrium water sorption in human stratum corneum,j. Pharrn. Sci.,
92, 1624-1631 (2003).
(22) G. Zografi, M. J. Kontny, A. Y. Yang, and G. S. Brenner, Surface area and water vapor sorption of
microcrystalline cellulose, Int. J. Pharrn., 18, 99-116 (1984).
(23) A. Jonquieres and A. Fane, Modified BET models for modeling water vapor sorption in hydrophilic
glassy polymers and systems deviating strongly from ideality, J. Appl. Polymer Sci, 67, 1415-1430
(1998).
(24) P. Lewicki, The applicability of the GAB model to food water sorption isotherms, Int.]. Food Sci. Tech.,
32, 553-557 (1997).
(25) M. M. Pradas, M. S. Sanchez, G. G. Ferrer, and J. L. Ribelles, Thermodynamics and statistical me-
chanics of multilayer adsorption,]. Chern. Phys., 121, 8524-8531 (2004).
(26) A. F. El-Shimi, and H. M. Princen, Water vapor sorption and desorption behavior of some keratins,
Colloid Polymer Sci., 256, 105-114 (1978).
(27) K. Walkley, bound water in stratum corneum measured by differential scanning calorimetry,]. Invest.
Derrnatol., 59, 225-227 (1972).
(28) B. Turek, M. Vieu, M. Leduc, I. Nadvornik, and E. Jedia, Water content and moisture-binding
capacity of some types of human soft and hard horn, Curr. Med. Res. Opin., 7, 87-90 (1982).
(29) A. Adamson, Physical Chemistry of Surfaces, 3rd ed. (John Wiley &Sons, New York, 1976), pp.
582-585.
(30) T. Yabuza, Creation of moisture sorption isotherms for hygroscopic materials, http://faculty
.che.urnn.edu!fscn!Ted_Labuza/PDF Jiles/Papers!Creation_Moistzm_jsotherrns.PDF, accessed 7 /3/06.
(31) C. Robbins, "The Physical Properties and Cosmetic Behavior of Hair," in Chemical and Physical Behavior
of Hurnan Hair, 3rd ed. (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1994), pp. 299-370.
(32) S. Wessel, M. Gniadecka, G. Jemec, and H. Wulf, Hydration of human nails investigated by NIR-
FT-Raman spectroscopy, Biochirn. Biophys. Acta, 1433, 210-216 (1999).
(33) C. W. Vertucci and A. C. Leopold, The relationship between water binding and desiccation tolerance
in tissues, Plant Physiol., 85, 232-238 (1987).
(34) F. J. Wortmann, P. Augustin, and C. Popescu, Temperature dependence of the water-sorption iso-
therms of wool,]. Appl. Polymer Sci., 79, 1054-1061 (2001).