JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 104 cause sunburn and to induce malignant melanoma (2). UV fi lters have been used as an ingredient in sunscreens to protect the skin from UVA and UVB. Most organic UV fi lters have effective protection against UVB but little effect against UVA, whereas butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane (USAN Avobenzone), terephthalylidene dicamphor sulfonic acid (USAN Ecamsule), and methylene bis-benzotriazolyl tetramethylbutylphenol (USAN Bisoctrizole) are utilized to protect UVA. Inorganic UV fi lters, such as TiO2 (USAN tita- nium dioxide) and ZnO (USAN zinc oxide) were combined in sunscreens to protect UVA. To improve protective effects from UV radiation, many cosmetic companies have tried to synthesize new UV fi lters or to develop certain formulation containing more than one UV fi lter (5–7). Although UV fi lters protect skin from UV radiation and help prevent skin damage including skin cancer, they are also concerned about the possibility of causing an allergic reaction to human skin (8). Studies reported that UV fi lters such as benzophenone-3 (Oxybenzone) and 4-methylbenxylidene camphor (USAN Enzacamene) exert the effects of endocrine disruptors (9,10). To prevent adverse effects of UV fi lters, many countries have regulated the amount of UV fi lters that will be used in sunscreens the maximum autho- rized concentration is 3–10% for organic UV fi lters (Table I) and 25% for inorganic UV fi lters. An easy and accurate analytical method for quantitation of UV fi lters is required to assure the label claims and maximum authorized concentrations in sunscreens. In some studies, UV fi lters were investigated using GC-MS or LC-MS, due to their trace levels in environmental or biological samples (11,12). However, in cosmetics, they were generally measured using a HPLC system connected to a UV detector. Although several studies de- scribed analytical methods of 11 or 16 organic UV fi lters using HPLC connected to a diode array detector, they employed different extraction solvents and several steps of extraction according to the cosmetic formulations (13–16). Sunscreens include UV fi lters as well as other ingredients such as emulsifi ers, solubility enhancers, and stability enhancers that are necessary for a cosmetic formulation and that might interfere with reliable analysis. Various chemical properties and physical properties of UV fi lters also make it diffi cult for them to be analyzed in sunscreens (17,18). Regarding various formulations of sunscreen such as cream, lotion, or powder, practical methods with a simple preparation are still needed for industry to develop a new product and for administrative bodies to monitor the quality for marketed sunscreens. The purpose of the present study was to develop a simple extraction method and a simultaneous analysis for 16 UV fi lters, including recent UV fi lters such as di- ethylhexyl butamidotriazone (USAN Iscotrizinol), methylene bis-benzotriazolyl tetramethyl- butylphenol (USAN Bisoctrizole), and terephthalylidene dicamphor sulfonic acid (USAN Ecamsule) (Figure 1). They were determined using HPLC connected to a C18 column and diode array detector (DAD) at 300, 320, and 360 nm. Method validation was achieved through specifi city, linearity, and recovery. Several solvents were examined for extracting UV fi lters from sunscreens, regardless of the matrixes used. The validated method was ap- plied to various types of sunscreens obtained from local markets and evaluated with regard to the label claims and compliance to their maximum authorized concentrations. EXPERIMENTAL MATERIALS Drometrizole (2440-22-4), menthyl anthranilate (134-09-8), benzophenone-3 (205-031-5), benzophenone-8 (131-53-3), octocrylene (6197-30-4), ethylhexyl dimethyl p-aminobenzoic
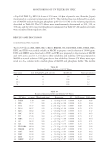
Table I Characteristics and Maximum Authorized Concentrations of UV Filters in the Present Study UV fi lter USAN name Abbreviation CAS # Molecular formula Molecular weight Max. authorized concentration (%) 1 Drometrizole Drometrizole DT 2440-22-4 C13H11NO3 225.25 —2 Benzophenone-8 Dioxybenzone BZ-8 131-53-3 C114H12O4 244.24 3% 4-Methylbenzylidene camphor Enzacamene MBC 36861-47-9 C18H 22 O 254.37 4% p-Aminobenzoic acid Aminobenzoic acid PABA 150-13-0 C7H7NO2 137.14 5% Butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane Avobenzone BMDM 70356-09-1 C20H22O3 310.38 5% Ethylhexyl triazone Octyl triazone EHT 88122-99-0 C48H66N6O6 823.07 5% Menthyl anthranilate Menthyl anthranilate MA 134-09-8 C17H25NO2 275.39 5% Ethylhexyl dimethyl p-aminobenzoic acid Padimate O ED-PABA 21245-02-3 C17H27NO2 277.40 8% 2-Phenylbenzimidazole-5-sulfonic acid Ensulizole PBS 27503-81-7 C13H10N2OS3 274.30 8% Benzophenone-3 Oxybenzone BZ-3 205-031-5 C14H12O3 228.25 10% Diethylhexyl butamidotriazone Iscotrizinol DBT 154702-15-5 C44H59N7O5 765.98 10% Ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate Octinoxate EMC 5466-77-3 C18H26O3 290.40 10% Isoamyl p-methoxycinnamate Amiloxate IMC 71617-10-2 C15H20O3 248.32 10% Methylene bis-benzotriazolyl tetramethylbutylphenol Bisoctrizole MBBT 103597-45-1 C41H50N6O2 658.88 10% Octocrylene Octocrylene OC 6197-30-4 C24H27NO2 361.48 10% Terephthalylidene dicamphor sulfonic acid Ecamsule TDS 92761-26-7 C28H34O8S2 562.69 10% 1 Maximum authorized concentration of UV fi lters is listed in Directive 76/768/EEC and in Notifi cation No. 2009-52 of the Korea Food and Drug Administration. 2 Maximum authorized concentration of Drometrizole is 7% in Korea. MONITORING OF UV FILTERS BY HPLC 105
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)