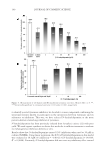
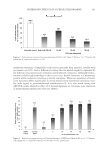
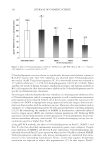
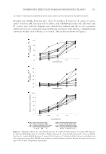
INHIBITORY EFFECTS OF KOREAN INDIGENOUS PLANTS 147 of the methanol extract was resuspended in 200 ml of water and was then extracted three times with the same volume of MC. The resulting aqueous layer was sequentially extracted with EtOAc and then n-BuOH using the same procedure as that used for MC extraction. The MC, EtOAc, n-BuOH, and aqueous layer were evaporated in vacua (VV2000, Heidolph, Schwabach, Germany), and approximately 1–20 g of powder or gel was obtained for testing (6,7). Table I List of Plants and Their TKM Names in Korea Scientifi c name TKM name Part used Chrysanthemum indicum Gamguk Flower Lonicera japonica Geumeunhwa Flower bud Vitex rotundifolia Manhyeongja Fruit Forsythia viridissima Yeongyo Fruit Evodia offi cinalis Osuyu Fruit Gentiana scabra Yongdam Root and rhizome Perilla frutescens (leaf and sprig) Jasoyeop Leaf and sprig P. frutescens (fruit) Jasoja Fruit Polyporus umbellatus Jeoryeong Sclerotium Houttuynia cordata Jeupchae Whole plant Celosia cristata Cheongsangja Seed Smilax china Tobokryeong Rhizome Prunus mume Omae Steamed and dried fruit Poncirus trifoliata Jisil Fruit Euonymus alatus Gwijeonu Alated sprigs Thuja orientalis Baekjain Seed Paeonia lactifl ora Jakyak Root Figure 1. The isolation of active fractions from plant samples.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 148 IN VITRO MUSHROOM TYROSINASE INHIBITION TEST Enzyme activity was determined by the method described by Ishihara et al. (8), modifi ed according to the results of preliminary testing to search for optimized conditions. Each of the extracts and fractions was dissolved in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and diluted to 1% individually. The solution was used as a test sample. Then, 20 μl of test solution, 220 μl of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5), 40 μl of 1.5 mM tyrosine, and 20 μl of 2000 unit/ml mushroom tyrosinase were sequentially transferred to a 96-well plate and incubated at 37°C for 10 min. The absorbance was measured at 490 nm with an ELISA reader (GENios, Tecan, Männedorf, Switzerland). As a blank solution, 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) was added, instead of test solution. IN VITRO INHIBITION OF L-DOPA AUTO-OXIDATION Enzyme activity was determined using the method described by Kong et al. (9), modifi ed according to the results of preliminary testing for optimized conditions. Each of the ex- tracts and fractions was dissolved in 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) and diluted to 1% individually. The solution was used as a test sample. Then, 20 μl of test solution, 220 μl of 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5), 40 μl of 500 μM L -DOPA (Sigma- Aldrich Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO), and 20 μl of 2000 unit/ml mushroom tyrosinase were sequentially transferred to a 96-well plate and incubated at 37°C for 10 min. The absorbance was then measured at 490 nm with an ELISA reader. As a blank solution, 0.1 M sodium phosphate buffer (pH 6.5) was added instead of test solution. CELL CYTOTOXICITY TEST Neutral red assay. Transformed mouse fi broblast L929 was inoculated into a 96-well plate containing Dulbecco’s modifi ed Eagle’s medium (DMEM) with 2% bovine calf serum (BCS) (3 × 103 cells/well) and incubated at 5% CO2 and 37°C for 48 h. The medium was then replaced with new serum-free medium containing transferrin (10 μg/ml) and ethanol- amine (2 μM) and again incubated for 48 h after the addition of sample dilutions. After incubation, 100 μl of neutral red (NR) solution (5 μg/ml) was added into each well and was allowed to react at 37°C for 3 h. After the reaction, the supernatant was removed and the solution was fi xed with 1.0% formalin containing 1.0% CaCl2 to immobilize cells for 5–10 min. After removal of the immobilization solution, 100 μl of 50% ethanol with 1.0% acetic acid was added to each well to extract pigments. The absorbance was then measured at 540–630 nm (double wavelength) with an ELISA reader to calculate the NR50. MTT assay. Transformed mouse fi broblast L929 was inoculated into a 96-well plate containing DMEM with 2% BCS (3 × 103 cells/well) and incubated at 5% CO2 and 37°C for 48 h. The medium was then replaced with new serum-free medium contain- ing transferrin (10 μg/ml) and ethanolamine (2 μM) and again incubated for 48 h after the addition of sample dilutions. After incubation, 100 μl of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol- 2yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) solution (5 mg/ml) was added to each well, and was allowed to react at 37°C for 4 h. After the reaction, the supernatant was removed and 100 μl of isopropanol containing 0.04 M HCl was added to each well to extract formazan from cells. The absorbance was then measured at 570–630 nm (double wavelength) with an ELISA reader to calculate the MTT50.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)