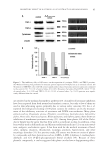
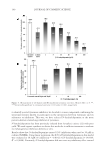
INHIBITORY EFFECTS OF KOREAN INDIGENOUS PLANTS 155 IN VIVO DEPIGMENTING EFFICACY TEST EtOAc fraction of P. lactifl ora and BuOH fraction of E. offi cinalis, which showed good results for the intracellular depigmenting effi cacy test, were selected as samples for the in vivo test. The samples and hydroquinone as a positive control dissolved in vehicle to 2% were evaluated for their topical effects on skin pigmentation of a brown guinea pig through daily application for 6 weeks of treatment. Results are shown in Figure 5. The P. lactifl ora fraction- and hydroquinone-treated sites showed skin-lightening effects as time increased, but the skin-lightening effect of E. offi cinalis was slight. From the view- point of adverse effects, P. lactifl ora- and E. offi cinalis-treated sites have shown slight skin irritation on one or two animals. In contrast, hydroquinone-treated sites showed signs of irritation after 2 weeks and these signs were more intense at 6 weeks. Figure 4. Inhibitory effects on (A) tyrosinase activity and (B) melanin biosynthesis in B16 melanoma cells (% of control). Results are shown as the averages ± SD of three independent experiments. *p 0.05 **p 0.01 compared to arbutin using a t-test.
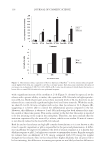
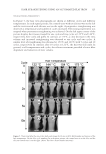
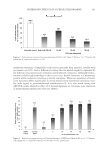
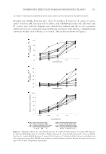
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 156 The degree of pigmentation on treated areas was measured according to the melanin index with a mexameter and is shown in the Figure 6. Both the EtOAc fractions of P. lactifl ora and hydroquinone resulted in a signifi cant skin-lightening effect com- pared to vehicle at 6 weeks. In conclusion, as a result of in vitro and in vivo depig- menting tests, the EtOAc fraction of P. lactifl ora was found to be the most effective substrate among the natural plant extracts. Figure 5. Representative photographs showing the depigmenting effect on UV-induced hyperpigmenta- tion: (A) vehicle, (B) 2% of P. lactifl ora fraction, (C) 2% of E. offi cinalis fraction, and (D) hydroquinone (positive control). Figure 6. The degree of depigmentation (Δmelanin index) before and 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 weeks after daily topical application of vehicle, 2% P. lactifl ora fraction, 2% E. offi cinalis fraction, and 2% hydroqui- none. Results are shown as the averages ± SD of three independent experiments. *p 0.05 compared to vehicle using t-test.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)