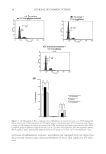
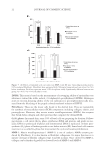
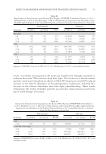
MOLECULAR MARKER APPROACHES FOR TRACKING REDOX DAMAGE 31 wools, was further investigated at the molecular marker level through sequential ir- radiation fi rst with UVA and then with blue light. The results for a keratin marker peptide containing tryptophan are shown in Table IV, showing an initial UV-induced increase in the relative abundance of the photoproduct, kynurenine, followed by a decrease in the relative abundance after blue light photobleaching. These results demonstrate the utility of marker peptides in proteomic characterization and track- ing of redox damage in keratins. Table III Dopa Formation From Tyrosine in the Keratin Wool Peptide, LASDDFR (Unmodifi ed Tyrosine m/z 823.4, Modifi ed Dopa m/z 839.4) After Blue Light, UVA or UVB Irradiation, Expressed as the Abundance of the Modifi ed Peptide Relative to the Unmodifi ed Peptide, as Assessed Using Ion Peak Intensity or Peak Area Peak intensity Peak area Treatment m/z 823.4 m/z 839.4 F*:F m/z 823.4 m/z 839.4 F*:F Blue light 3 h 226 152 67.3 26.2039 20.8936 79.7 24 h 64 59 92.2 8.3824 8.2307 98.2 72 h 97 125 128.9 10.9161 14.9627 137.1 UVA 3 h 1332 1079 81.0 208.2376 173.0123 83.1 24 h 283 284 100.4 45.3400 46.4632 102.5 72 h 44 66 150.0 4.1464 5.7242 138.1 UVB 3 h 103 47 45.6 11.3387 4.7810 42.2 24 h 104 111 106.7 12.6693 17.5339 138.4 72 h 94 156 166.0 9.1246 16.7719 183.8 Sequence: LASDDFR Location: K1M2 res 135-141 Modifi cation: F→Y. F* is the modifi ed residue. Table IV Kynurenine Formation from Tryptophan in the Keratin Wool Peptide, DVEEWYIR (Unmodifi ed m/z 1109.5, Modifi ed m/z 1113.5) After 24 h UVA Irradiation and Varying Periods of Blue Light Irradiation, Expressed as the Abundance of the Modifi ed Peptide Relative to the Unmodifi ed Peptide, as Assessed Using Ion Peak Intensity or Peak Area Peak intensity Peak area Treatment m/z 1109.5 m/z 1113.5 W*:W m/z 1109.5 m/z 1113.5 W*:W UVA 24 h 166 63 38.0 28.5065 11.3454 39.8 24 h UVA + blue light 24 h 43 40 93.0 2.1699 3.5685 164.5 48 h 2193 745 34.0 769.7623 328.7012 42.7 72 h 1670 537 32.2 286.9957 96.5852 33.7 Sequence: DVEEWYIR Location: K1M1, K1M2 res 241-248 Modifi cation: W→[W+2O-CO]. W* is the modifi ed residue.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 32 Table V Change in Yellowness (Y-Z) in Wool Fabric Irradiated for 72 h with UVA, UVB, or Blue Light, with Statistical Error Presented as One Standard Deviation (SD) Irradiation type Y-Z score SD Control (unirradiated) 7.73 0.70 UVA 13.57 0.80 UVB 22.79 1.54 Blue 6.40 0.49 Table VI Keratin Photomodifi cations Characterized in 72 h UVA Irradiated Whole Wool (Modifi ed residues underlined) Monoisotopic m/z Charge Sequence Modifi cation Tryptophan 854.34 1+ AEAEAWY Oxidation (W) Protein ID Type II K82 855.33 1+ DVEEWY Oxidation (W) Protein ID Type I K31K33a, K33b, K34 1200.53 2+ WQFYQNQR Formylkynurenine (W) Protein ID Type II K85 1867.68 3+ SCNWFCEGSFDGNEK Formylkynurenine (W), Carbamidomethyl (C) Protein ID Type I K31, K33a, K33b, K34 721.26 1+ AEAESW Tryptophandione (W) Protein ID Type II K81, K83, K85, K86, K87 747.28 1+ AEVESW Bis-tryptophandione Protein ID Type II K85(Bos taurus) 1220.62 2+ LLETKWQLY Bis-tryptophandione Protein ID Type II K85, K87 Tyrosine 966.46 2+ LYEEEIR Hydroxylation (Y) Protein ID Type II K81, K86, K87 982.45 2+ LYEEEIR Dihydroxylation (Y) Protein ID Type II K81, K86, K87 1023.48 2+ YEEEVALR Hydroxylation (Y) Protein ID Type II K81, K85, K86 1053.47 2+ AQYDDIASR Hydroxylation (Y) Protein ID Type II K81, K83K85 1069.45 2+ AQYDDIASR Dihydroxylation (Y) Protein ID Type II K81, K83, K85 1151.58 2+ KYEEEVALR Hydroxylation (Y) APPLICATION TO A COMPLEX PROTEIN SYSTEM: DAMAGE AND PROTECTION OF WHOLE WOOL The next step was to apply and validate the tracking of redox modifi cation in marker peptides to a complex proteinaceous system, in this case wool fabric. The dry weight of wool comprises approximately 98% proteins, with about 60% of the total weight being derived from keratins (18,19). The keratins are also the key structural proteins in skin,
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)