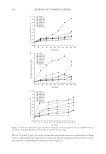
EVALUATION OF MOLECULES OR EXTRACTS MODULATING SEBORRHEA 191 as they constitute a natural front line of defense against bacteria, virus, and fungi prolif- eration. We showed that NHS produced more cathelicidin and hBD2 in presence of CCSV than in the negative control. These two natural small proteins, with broad spectrum antimicrobial activity, were increased in a dose response manner (Table VIII) by 0.16 and 0.48 mM CCSV, respectively, by +17% and +39% (both p 0.01) and by +25% and +47% (nsd p 0.01). These increases were in line with pro-infl ammatory modula- tions (Tables II–VI). IN-VIVO STUDIES Sebum production and number of active glands were evaluated after 1 month of applica- tion of placebo cream or cream containing 0.8 mM CCSV. The analysis of the results demonstrated that placebo did not induce a variation whatever the studied parameter. In contrast, use of 0.8 mM CCSV for 1 month led to a signifi cant decrease both in the quantity of sebum produced and in the number of active glands whether compared with T0 (-15% for both) or placebo: -18% (p 0.05) and -15.8% (p 0.05), respectively (Table IX). Hyperkeratinization was evaluated through two complementary methods: SCTE labeling into skin explants and cyanoacrylate biopsies of stratum corneum. Results showed an increase (+40%) in SCTE labeling on skin sections after a daily application of cream con- taining 0.8 mM CCSV versus placebo cream (19.75 ± 1.75 vs. 14.1 ± 1.6 p 0.01 vs. placebo). Moreover, microscopic assessment of the hyperkeratosis performed after stain- ing (see materials) indicated that 83% of responders (10/12) experienced a decrease in their keratosis, whereas two of them experienced an increase. Skin blemishes were evaluated on several panels due to the diffi culty in recruiting volun- teers with blemishes (see Materials). In the fi rst study, there was an observed 38% de- crease in the surface area of red blemishes (46.0 ± 28.2 → 28.6 ± 22.1 p 0.01 vs. placebo, n = 12 Figure 5) and a high response level of 83%. In contrast, applying a pla- cebo for 1 month led to no improvement of skin appearance. First results were confi rmed in a second test (Cosmetest®). Dermatologist counting of blemishes indicated a 48% Table VIII Cathelicidin and hBD2 Variation by NHS in Contact with CCSV. No Cell Toxicity Was Observed as Compared to Control Cathelicidin (pg/ml/106 cell) hBD2 (pg/ ml/106 cell) Negative control 342 ± 8 42.0 ± 11.1 CCSV 0.16 mM 401 ± 23 52.5 ± 8.1 CCSV 0.48 mM 474 ± 29 61.6 ± 4.1 Table VII NO Release by RAW 264.8 in Contact with LPS and CCSV NO (μM/106 cell) Control 49 ± 2.0 CCSV 0.16 mM 29 ± 2.0 CCSV 0.48 mM 22 ± 1.0
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 192 decrease in the number of infl amed skin blemishes (7.08 ± 3.50 → 3.67 ± 2.64 p 0.01 vs. placebo, n = 12). In parallel, placebo cream applied for 1 month did not signifi cantly improve skin appearance, confi rming fi rst results. Third evaluation (Cosmetest®) showed a 21% decrease in the number of retentional lesions (13.65 ± 11.96 → 10.78 ± 9.57 p 0.01 vs. T0, n = 23, dermatologist). Conversely, there was no signifi cant improvement on the placebo side. A self-evaluation questionnaire was fi lled by a panel of 100 women and men (mean: 24 years, [18–30 years]) claiming to have acne-prone oily skin and regularly occurring pimples. They analyzed the cosmetic qualities and activities of a cream containing 0.8 mM CCSV applied once a day for 1 month. Figure 6 shows results demonstrating the positive perception of the product and highlighting the multiple effects perceived by the volunteers (e.g., less redness, less shininess, less severe pimples). DISCUSSION/CONCLUSION Complementary biological models and methods are of interest for the study of highly complex skin phenomena such as seborrhea and its consequences. In vivo studies are es- sential to validate the effect of active molecules but clinical evaluations are not appropri- ate for the selection of candidates. However, only a few sebocyte models now exist to screen and to study the effect of molecules aside from cell lines. The development of a NHS primary culture allows focusing more physiologically on lipid metabolism under the contact of both positive and negative modulators of lipid synthesis such as linoleic Table IX Sebum Production and Number of Active Glands after 1 Month, n = 23 vol. Placebo Cream or Cream with 0.8 mM of CCSV Sebum production (spot area in mm²) Variation 1 m vs. T0 Number of active glands Variation 1 m vs. T0 T0 T1 m T0 T1 m Placebo 1.45 ± 0.85 1.49 ± 0.98 +2.8% nsd 341 ± 155 345 ± 158 +1.2% nsd CCSV 1.51 ± 0.92 1.28 ± 0.86 -15,2% p 0.05 384 ± 157 328 ± 154 -14.6% p 0.09 Signifi cance CCSV vs. placebo p 0.05 – p 0.05 Figure 5. Skin blemishes after 1 month, n = 12 vol. cream with 0.8 mM of CCSV.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)