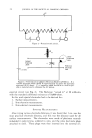
DEGERMING ACTIVITY OF TOILET BARS 411 environmental conditions. The bacteria removed with each succeeding wash become more characteristic, and these are described as resident bac- teria capable of thriving on skin. If a sufficiently large number of washes is done, the number of resident bacteria removed per basin becomes rela- tively constant for a given subject. Since a large number of washes to determine this constant value is impractical and the resident bacteria pre- dominate after the fourth or fifth wash (Fig. 1) the counts of the fourth and/ 6 0 4 8 12 16 20 30 NUMBER OF BAS INS Figure 1.--Effect of serial basin wash procedure on hand bacterial counts. or fifth basin are usually taken as a fairly reliable measure of the cutaneous bacterial count. With this value as a point of reference the effectiveness of a germicidal soap, which is used regularly over a period of one or two weeks, can be determined by observing whether the counts for the fourth and/or fifth wash waters decrease significantly. The test procedure used to obtain most of the data discussed in this paper is one of expediency. The greatest variability in the test is among sub- jects, and the maximum convenient number of subjects is used, usually 12. Only subjects regularly using plain soap are selected. Hands and half the forearms are washed under running tap water three times. The hands are soaped for fifteen seconds, lathered for one minute, and rinsed for fifteen seconds. The fourth wash, up to the wrist bone only, is done in a basin containing two liters of sterile tap water. Duplicate one ml. samples are plated out in nutrient agar, the plates incubated forty-eight hours at 37øC., and the colonies counted. This count multiplied by 2000 represents total number of bacteria •emoved from the hands. The same procedure is done the following day, and the average count of the fourth basins on each day is taken as the initial count (I). The subjects are then given the test soap for regular use at home and at work for a period of one week. The only instructions are to use the bar at
412 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS least three times daily and avoid the use of other products during the test period. Contact with organic solvents and antiseptics is prohibited. No special directions for use are given to the subjects who follow their regular wash habits. At the end of one week, fourth basin counts are obtained on two successive days, using plain soap for the four washes each day. The average of these two counts is the final count (F). The difference between the average basin counts before and after use of the test bar is a measure of the effectiveness of the degerming activity of the deodorant bar, and is usually expressed as per cent reduction. TABU• 1--SERIAL BASIN WASH Tes'r Sou}tcss or VARIATION Plate to plate Day to day Basin to basin Week to week Subject to subject The obvious sources of variation in the test are listed in Table 1. Since the day to day variation is sometimes appreciable, counts are taken on two successive days. In comparison, the basin to basin (e.g., fourth and fifth basins on the same day) variation is small and only one basin per day is sufficient to obtain a reliable estimate of cutaneous count. The plate to plate variation is negligible but duplicate plates are made to insure against occasional contamination. The greatest source of variation is that between subjects, and a compromise is made in using the largest number of su•ects TABLE 2--COMPUTATION OF PEa CENT REDUCTIONS Rule 1. Whenever there is a higher final count, assign a per cent reduction value of zero otherwise, compute by Rule 2. Rule 2. Compute the per cent reduction in the usual way -- X lOO I where ] and F are the initial and final counts, respectively. Rule 3. When F is greater than I, compute the per cent reduction as X 100 F Bacterial Counts Per Cent Reductions Initial Final Rule 1 Rule 2 Rule 3 Per Cent Reductions as Computed by Each of Three Rules 500 50 90 90 90 1500 300 80 80 80 2500 1250 50 50 50 900 675 25 25 25 675 900 0 - 33 -25 1250 2500 0 -- 100 -50 300 1500 0 --400 -80 50 500 0 --900 --90 Average 30.6 - 148.5 0
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)