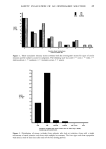
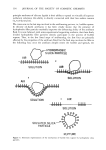
THE ANALYSIS OF OMADINE © BY LIQUID CHROMATOGRAPHY 75 B A D 0246810 TIME (MIN) Figure 1. Separation of 2-pyridinethiol (A), 2,2'-dithiobispyridine-l,l'-dioxide (B), 2-pyridinesulfonic acid-l-oxide (C), and 2-pyridinesulfonic acid (D). Mobile phase: 15:85 acetonitrile/H20 containing 5 ml/l of 40% tetrabutylammonium hydroxide solution, 4 ml/1 glacial acetic acid and 0.5 ml/l of saturated Na2EDTA. Flow rate: 1.5 rnl/min. Sensitivity: 0.01 AUFS for A,C,D 2.0 AUFS for B. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION A single isocratic separation was first developed for all five compounds. Tetrabutylam- monium hydroxide was used as an ion pairing agent for the purpose of retaining PSA and OMSA. An amount of acetic acid was added sufficient to adjust the pH to 3.7, at which the sulfonic acids would be ionized, and thus form ion pairs, while the 2-pyridinethiol would not. At this pH, also, the two disulfides are quite stable. Since OMDS has some tendency to form metal complexes, Na2EDTA was added to the mobile phase to prevent low recoveries and spurious peaks. Depending upon the separation desired, the composition of the mobile phase was varied with respect to the acetonitrile: water ratio however, the concentration of ion-pairing agent, pH adjustor and complexing agent were kept constant. The separation of 2MP, OMDS, OMSA and PSA in a clear shampoo formulation is shown in Figure 1. The simultaneous analysis of all four compounds in a single chromatogram requires that the full scale sensitivity be changed during the chromato-
76 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I Recovery Of 2,2'-Dithiobis-Pyridine-l,l'-Dioxide In Clear Shampoo % OMDS Spike % OMDS Found % Recovery 1.214 1.206 99.3 0.9758 0.9665 99.0 1.048 1.039 99.2 1.125 1.117 99.4 1.050 1.065 101.5 1.077 1.062 98.9 x = 99.55 RSD = 0.97% graphic run. This is necessary because OMDS is generally present at close to 1% while the other compounds are present in much lower concentrations. Accordingly, the attenuation is set at approximately 0.005 AUFS until 2MP has been eluted and then changed to 2.0 AUFS before the elution of OMDS. After OMDS has been eluted the sensitivity is again greatly increased. OMDS ANALYSIS Table I shows the recovery data with the relative standard deviation (RSD) for a commercial blank shampoo formulation spiked with approximately 1% OMDS. The recovery and precision of several commercial shampoos compare favorably with polarographic results which appear in Table II. For many of the samples, the polarographic value is several hundredths of a per cent higher than the LC value. This may be due to the fact that the LC method is specific for OMDS, while the polarographic method measures "total disulfide." Great care must be taken to remove oxygen from the polarographic cell since its presence will also lead to erroneously high results. OMSA AND PSA As shown in Figure 1, OMSA and PSA are well retained and easily separated by the ion-pairing technique. Although in this chromatogram OMSA is slightly affected by the tailing of the OMDS peak, the recovery and precision, as shown in Tables III and Table II Analysis Of Clear Shampoos For 2,2'-Dithiobis-Pyridine-l,l'-Dioxide Via HPLC And Polarography % OMDS Sample HPLC Polarography 873406 0.90 0.92 873405 0.89 0.91 A22435B 0.32 0.32 A22435C 0.53 0.57 A22487A 0.56 0.56 873286A 0.23 0.26 873281A 0.53 0.60 873286B 0.089 •.093
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)