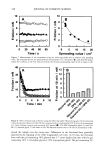
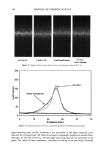
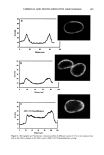
AMMONIA/PEROXIDE BLEACHING OF HAIR 403 Figure 5. ESEM image of a suspension of Sepia melanin (x4000). A suspension of 0.05 mg/ml of Sepia melanosomes was used for the ESEM imaging studies. intact melanosomes were visible by TEM image analysis. However, after 2-3 hr of treatment, structural changes leading to the dissolution of melanin granules were ob- served. The changes were slightly faster at pH 8.0, and prolonged treatment led to a clear solution, indicating that bleaching has occurred. The study clearly suggests that neutral H202 is less efficient than NH 3 in inducing morphological and structural changes to hair melanosmes. TEM STUDIES ON THE EFFECT OF AMMONIA/PEROXIDE Time-dependent TEM imaging studies were performed on isolated hair melanosomes (0.05 mg/ml) after treatment with NH 3 (1%) and H202 (1%) at pH 10. Co-treatment with NH 3 and H202 induced a faster disintegration of melanosome particles, and structural changes were visible even after 10 min of treatment. Figure 9 shows the TEM image of ammonia/peroxide-treated hair melanosomes after 15 min of treatment. In contrast to the effect of ammonia, co-treatment with ammonia and peroxide induced a simultaneous disintegration and dissolution of melanosomes. The overall disintegra- tion, dissolution, and discoloration process is much faster than ammonia treatment due
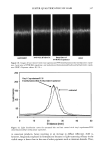
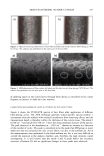
404 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE ß 904.47 100 nm Figure 6. TEM image of isolated hair melanosomes from Asian black hair (x75,000). A sonicated suspen- sion of hair melanosomes (0.05 mg/ml) in water at neutral pH was used for the TEM imaging study. to oxidative attack by hydrogen peroxide. Thus, it is clear from the study that the role of ammonia is to help the release of melanin nanoparticles from the melanosomal sac, making it more susceptible to attack by peroxide. At the end of 30 min, the ammonia/ peroxide-treated melanosome suspension gave a colorless solution devoid of any particles, while ammonia treatment gave a yellow-colored suspension, clearly indicating that the role of peroxide is to decolorize the degraded melanosomes. DISCUSSION Chemically unaltered melanosomes from Asian black hair were isolated using a mild enzymatic procedure involving sequential treatment of a hair sample with different protease enzymes (1). The UV-Vis absorption spectrum of hair melanosome suspension in water showed a structureless spectrum with absorptivity increasing monotonically with decreasing wavelength, characteristic of natural and synthetic melanins. Both Sepia
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)