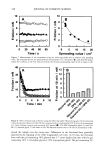
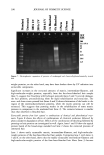
416 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table I D-Values and Correlation Coefficients of the Preservative Efficacy Test for Bacteria Test S. aureus P. aeruginosa Preservative No preservative Preservative No preservative D-value R D-value R D-value R D-value R 1 12.0 2 14.9 3 16.1 4 14.5 5 13.7 6 10.1 M_+ SD 13.6_+ 1.97 0.9938 57.8 0.9603 13.1 0.9999 16.3 0.9751 0.9963 -- 0.7309 9.8 0.9892 13.1 0.9805 0.9997 133.3 0.9924 13.2 0.9472 14.8 0.9897 0.9993 -- 0.6423 22.1 0.9570 13.9 0.9927 0.9635 294.1 0.9896 14.3 0.9978 14.1 0.9813 0.9990 -- 0.4672 13.9 0.9921 18.2 0.9912 161.7 _+ 98.54 14.4 + 9.15 15.1 + 4.2 M + SD: Mean + standard deviation. Table II D-Values and Correlation Coefficients of the Preservative Efficacy Test for Fungi C. albicans A. niger Preservative No preservative Preservative No preservative Test D-value R D-value R D-value R D-value R 1 4.6 0.9420 -- 0.0458 0.000 -- 0.1726 2 4.3 0.9706 -- 0.2421 0.000 0.4079 3 4.4 0.9886 -- 0.0400 0.8891 0.8807 4 4.0 0.9888 -- 0.1095 -- 0.2121 -- 0.3375 5 7.3 0.9011 21.6 0.9199 0.4064 -- 0.1300 6 6.8 0.9846 -- 0.8323 0.8755 0.5704 7 3.8 0.9946 19.9 0.9942 -- 0.0922 NE NE 8 4.4 0.9960 25.2 0.9700 NE NE NE NE M + SD 4.95 + 3.51 22.23 + 3.83 NE: Not executed. M + SD: Mean + standard deviation. It was possible to determine the average D-values for S. aureus and C. albicans in samples with preservative, but samples without preservative did not have good correlation co- efficients (Tables I and II). Mean D-values were 13.6 hours and 4.95 hours, respectively. Nevertheless the D-values showing good correlation, for both cases presented lower rates when using the preservative compared with the others. The analysis of variance for the two different treatments (with and without preservative) for S. aureus confirms that samples with preservative presented different behavior com- pared to samples without preservative, providing an F-value of 10.54 and a critical F-value of 5.11. For C. albicans, the F-value was 217.51 and the critical value was 5.12, showing again that the two different groups are different (Table III). For P. aeruginosa (Table I), the average D-values were almost the same for the tests with and without preservative: 14.4 hours and 15.1 hours, respectively. The comparison between the two treatments showed no difference, providing an F-value of 0.131 and a
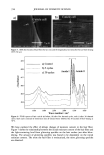
PRESERVATIVE EFFICACY TESTING METHOD 417 Table III Statistics Data Comparing D-Values in Preserved and Unpreserved Powders Microorganism F-value Critical F-value Staphylococcus aureus 10. 54417 5.59146 Pseudomonas aeruginosa O. 131475 4.964591 Candida albit•ns 217.5148 5.117357 critical F-value of 4.96 (Table III). However, in Figure 6, one can observe that the curves constructed for the tests with preservative presented a steeper slope (i.e., faster die-off) than the ones for the tests without preservative. Such behavior can also be seen for S. aureus and C. albicans (Figures 6 and 7). LogCFU/õ 5 1- 0 0 $ Time (days) a Lag CFUIg Time (days) Log CFU/g o 5 Log CFUlg 7- 6- •) 15 3) 2• 3) 0 5 10 15 39 25 3:) Time (days) Time (days) c d Figure 6. Survival curve of bacteria in the sample with preservative (P) and without preservative (NP). (a) S. aureus, sample P. (b) S. aureus, sample NP. (c) P. aeruginosa, sample P. (d) P. aeruginosa, sample NP.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)