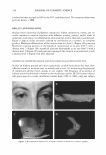
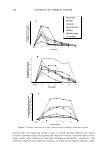
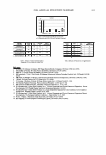
2004 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC SEMINAR 419 SPF/% Ti02 2.34 2.11 U3 3.56 3.17 3.08 1.73 1.05 0.71 Critical Lambda 317.31 .... 370.2 310 379.51 3I0.2 371.1 371.8 37'.05 -- UVA/UVB UM 0.48 0.437 0.701 0.703 0�709 O.MI 0..514 0,531 SPF Change (t)2U%. (·) 0.S'lft ( ·} 11'- ,� ( : 13;5� (·)39.3% (-) 59"4 Table 4. Comparison of powder performance versus addition of dispersions to oil phase or final emulsion Looking more closely at the amphiphilic dispersion of the hydrophilic Titanium Dioxide in the amphisoluble polyether, PEG 7 Methyl Ether, optimal performance occurs with addition to the emulsion continuous phase favoring effective dispersion in the outer phase with less dependence on emulsion breakdown on skin and coalescence of sunscreen micropigment laden droplets. See Table 5.below. Properties SPF/%Ti02 Critical Lambda UVA/UVB SPF/% Ti02 Critical Lambda UVA/UVB SPF/% TI02 Critical Lambda UVA/UVB Table 5. Dispersion of Hydrophilic Titanium Dioxide in Polyether (PEG 7 Methyl Ether) Performance of polyether dispersion is significantly better in hydrophilic O/W emulsion but not in gel network or inverse water-in-silicone emulsion. See Table 6. below
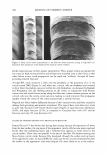
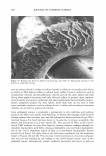
420 Properties Dispersion (3) in PEG7 Methyl Ether SPF/%TiO2 Critical Lambda UVA/UVB SPF Change SPF/%TiO2 Critical Lambda UVA/UVB SPF Change SPF/%TiO2 Critical Lambda UVA/UVB SPF Change JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE In TiO2 in oil Dispersion phase, solvent added last In water phase U1 U1 1.39 2.64 312.4 ., .. 3B1.5 381.65 .. ,. 0,711 0.717 0.757 UI 1.21 NIA 1.51 aJUI NIA 381.2 NIA 0.705 317 NIA 3.08 171.111 N/A 380.2 NIA 0.709 Table 6. Polyether (PEG 7 Methyl Ether) dispersion versus controls added to water phase, oil phase or final emulsion. Overall, both performance and aesthetic aspects, especially transparency as demonstrated by draw down films and skin application, point to control by parameters of the initial inorganic pigment chosen for UVR attenuation and the way it is dispersed in the skin film. Methods need to advance to the stage where skin film particle size and SPF can be determined simultaneously site by site for more accurate assessment of film differences. Even within the scope of current technology, additional experiments need to be conducted to support the hypothesis that optimal performance occurs with optimal dispersion in the product film after rub in and dry down on the skin. Directionally, these preliminary results point to getting the active particles well dispersed in the continuous phase that lays down on the skin. But this is also linked to the nature of the emulsion as it breaks down on the skin and where those particles eventually go to effectively absorb, reflect and diffract UVR with limited effect on visible light to make their efficacy invisible.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)