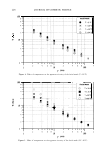
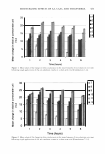
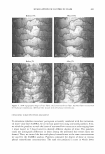
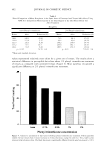
FCP DESCRIPTIVE ANALYSIS OF STICK BASES 463 (13) A. Gambaro, A. Gimenez, P. Varela, and E. De Penna, Association of strawberry yogurt sensory properties with product composition by procrustes analysis,]. Sens. Stud., 19, 293-326 (2004). (14) R. J. Marshall and S. P. J. Kirby, Sensory measurement of food texture by free-choice profiling,]. Sens. Stud., 3, 63-80 (1988). (15) Gels & stick documentary, Cosmet. Toiletr., 102, 53-63, 119-124 (1987). (16) Gels/stick formulary, Cosrnet. Toiletr., 114, 68-89 (1999). (17) G. Barket, Sodium stearate-based stick: Proposed structure, Cosmet. Toiletr., 102, 71-80 (1987). (18) N. Geria, Manufacturing and packaging technology of OTC and cosmetic stick, Cosmet. Toiletr., 102, 65-70 (1987). (19) ISO 8589, Sensory Analysis: General Guidance for the Design of Test Rooms (International Standards Organization (ISO), Switzerland, 1988).
J. Cosmet. Sci.! 57, 465-473 (November/December 2006) Comparing the moisturizing effects of ascorbic acid and calcium ascorbate against that of tocopherol in emulsions U. GONULLU, D. SENSOY, M. UNER, G. YENER, and T. ALTINKURT, Istanbul University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Beyazit 34119, Istanbul, Turkey. Accepted for publication August 25, 2006. Presented as a poster at the Skin and Formulation Symposium organized by APGI (Association de Pharmacie Galenique Industrielle), Paris, October 23-24, 2003. Synopsis Calcium ascorbate (CAAS), which is a hydrophilic and stable derivative of ascorbic acid (vitamin C) (AA), is commonly used in foods as an ancioxidative agent. There are very limited reports on its dermatological use in the literature. In this paper, it is reported that CAAS could be used in place of ascorbic acid, which has chemical stability problems in topicals due to degradation by oxidation. The aim of this study was to investigate the skin-hydrating effect of CAAS compared to those of ascorbic acid and tocopherol (vitamin E) (T), which is a potential skin moisturizer and commonly used in dermocosmetics. Vitamins are incor porated into two kinds of base creams (o/w and w/o emulsion creams), alone and in combinations. Formu lations were applied to the inner forearms of volunteers, and skin conductance was measured by using a corneometer. Data obtained were statistically evaluated. It was found that the skin-hydrating effect of CAAS was higher than that of AA and lower than that of T. However, its effect was very close to that of T. INTRODUCTION Skin care products are designed with the intention of improving skin conditions. Two ways to provide this is by increasing skin hydration or by stimulating the synthesis of collagen and elastin fibers. Antiaging compounds that are antioxidants and/or collagen metabolism activators are some of the actives that are used in formulations with this aim (1,2). Ascorbic acid (AA), AA derivatives, and tocopherol (T) mainly act as potent free-radical scavengers (3-5). Free oxygen radicals are highly reactive chemical species that are generated in cells and tissues by sunlight, tobacco smoke, and also by normal metabolic processes that involve oxygen from the atmosphere. They can cause damage to the lipids, proteins, and nucleic acid inside the cell, endandering tissue integrity (6-9). Free radicals are thought to be Address all correspondence to U. Goniillii 465
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)