J. Cosmet. Sci., 60, 519–525 (September/October 2009) 519 High-performance liquid chromatography with dual- wavelength ultraviolet detection for measurement of hinokitiol in personal care products YASUHIKO HIGASHI, MASATOSHI SAKATA, and YOUICHI FUJII, Department of Analytical Chemistry, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Hokuriku University, Ho-3, Kanagawa-machi, Kanazawa 920-1181, Japan. Accepted for publication March 26, 2009. Synopsis Hinokitiol is found in the heartwood of several cupressaceous plants and is frequently added to cosmetic products such as hair restorers, skin lotions, and body soaps because of its potent and broad-spectrum anti- bacterial activity. In this study, we established a simple method of hinokitiol determination by high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with dual-wavelength ultraviolet detection at 240 and 345 nm, using a reversed-phase C4 column (RP-4). The retention time of hinokitiol was 7.1 min at both wavelengths. The value of the symmetry coeffi cient of the hinokitiol peak was close to 1 when the RP-4 column, not an RP-8 or RP-18 column, was used. With the RP-4 column, the regression equation for hinokitiol showed good linearity in the range of 0.05–5 μg/ml, with a detection limit (signal-to-noise ratio of 3) of 0.005 μg/ml at 240 nm and 0.01 μg/ml at 345 nm. The coeffi cients of variation at 240 and 345 nm were less than 8.2% and 8.7%, respectively, and the recovery was good. The proposed method was used for the determination of hinokitiol in commercial hair restorers, skin lotions, and body soaps. INTRODUCTION Hinokitol (Figure 1, β-thujaplicin, 4-isopropyl-2-hydroxycyclohepta-2,4,6-trien-1-one) is a naturally occurring toxic compound belonging to the class of tropolones that contain an unsaturated seven-membered carbon ring. The compound is found in the heartwood of several cupressaceous plants, such as western red cedar (Thuja plicata), eastern white cedar (Thuja occidentalis), hinoki cypress (Chamaecyparis obtusa), and hiba (Thujopsis dola- brata) (1,2). Since hinokitiol has potent antibacterial and antifungal activities (minimum inhibitory concentration of 0.2 μg/ml for Staphylococcus epidermidis and Daedalea dickinsii) (2,3), it is added to products such as hair lotions, skin lotions, and body soaps, among other cosmetics. Little work has been reported on the gas chromatography (GC) or high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) of hinokitiol because the tropolone ring has a chelating Address all correspondence to Yasuhiko Higashi.
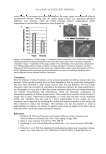
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 520 property, is unstable to heat, and tends to be adsorbed on the stationary phase. Quantita- tive determinations of hinokitiol by GC and capillary GC have been performed after de- rivatization with trimethylsilyl chloride and with diazomethane, respectively (1,4). Hanafusa et al. (5) reported the determination of hinokitiol in cosmetics by HPLC with ultraviolet (UV) detection following the formation of hinokitiol-copper(II) complex by addition of copper(II) to the mobile phase. However, the sensitivity of these methods was not discussed. Further, it is time-consuming and laborious to treat waste containing copper(II). A sensitive HPLC determination of hinokitiol based on the formation of di- fl uoroborane compounds was reported to have a detection limit of 40 pg of hinokitiol (6). Recently, hinokitiol was determined using a capillary zone electrophoresis method, which provided a detection limit of 0.21 μM (7). In this paper, we compared the HPLC determination of hinokitiol with RP-4, RP-8, and RP-18 columns. The method using RP-4 was applied for the measurement of hinokitiol levels in a hair restorer, a skin lotion, and a body soap. EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS The HPLC system comprised a model LC-10AT pump (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), a Rheodyne injection valve (Cotati, CA, USA) with a 200-μl loop, and a model SPD-10A dual UV detector (Shimadzu) operated at 240 and 345 nm. The HPLC columns (150 mm × 4.6 mm, Mightysil® RP-4, RP-8, and RP-18 GP, Kanto Chemical, Tokyo, Japan) were packed with 5-μm particles of C4, C8, and C18 packing materials, respectively. Quanti- fi cation of the peaks was performed with a Chromatopac Model C-R8A integrator (Shimadzu). REAGENTS Hinokitiol was obtained from Tokyo Chemical Industry (Tokyo, Japan). General reagents were obtained from Wako Pure Chemical Industries (Osaka, Japan). The tested hair re- storer, skin lotion, and body soap were purchased from markets. Figure 1. Chemical structure and UV absorption spectrum of hinokitiol.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)