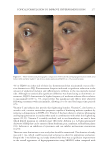
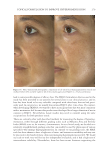
Supplementary table I Current approaches for topical skin Anti-aging formulations Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. Formulation and evaluation of curcumin gel for topical application Conventional (gel) Curcumin Viscosity measurement was determined by using a Brookfi eld viscometer (70) Franz diffusion cells was used for in vitro skin permeation study Visual assessment of skin irritation in Wistar albino rats was performed by using visual scoring scale Evaluation of the anti-infl ammatory effect of the optimized formulations was detected by using carrageenan-induced rat paw edema method Preparation and evaluation of submicron carriers for NGN topical application Submicron emulsion Naringenin Viscosity measurement was determined by a cone-and-plate rheometer (92) Measurement of the droplet size was measured by the DLSa technique In vitro skin permeation studies were conducted via Franz diffusion cells Drug deposition in SCb, epidermis, and dermis was determined via HPLCcafter layer separations: (the SC was removed using an adhesive tape, and theepidermis was separated from the dermis by heat) Histological evaluation of skin irritation in male Sprague–Dawley rats was performed. Physical, chemical, and thermodynamic short-term stability studies had been conducted SKIN-AGING AND INFLAMMAGING TREATMENT 343
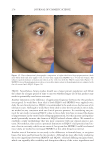
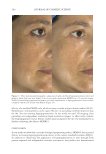
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. CoQ10and retinaldehyde co-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for effi cacy evaluation in wrinkles Gel containing nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) loaded with CoQ10 and retinaldehyde CoQ10and Retinaldehyde In vitro physicochemical characterization: (141) Examining the NLCscolloidal d system morphology was performed by SEMe Evaluating both the free gel and the NLCs containing gel spreadability and rheological behavior were determined by the cone-and-plate viscometer HPLC-based stability study A comparative drug release study was performed from NLCs and NLCs-gel In vitro cell culture studies were carried out for both cellular uptake and viability Ex vivo studies were carried out for assessment of skin permeation, distribution and dermal pharmacokinetics In vivo study was conducted by using animal model The skin irritation test on Sprague-Dawley rats was performed by using a vapometer to measure trans epidermal water loss Evaluating the therapeutic effi cacy of the optimized formulations on female Swiss albino mice after wrinkles induction Supplementary table I Continued JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 344
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)