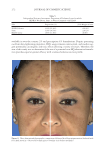
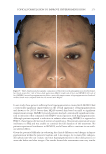
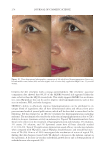
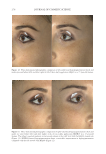
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. Transdermal delivery of functional collagen via polyvinylpyrrolidone microneedles Polyvinylpyrrolidone microneedles Collagen type 1 Examination of the microneedle morphology was detected via SEM and CLSMq. (77) Collagen type 1 was separated via SDS-PAGE electrophoresis Functional collagen concentration was determined via ELISAr Microneedle penetration through the porcine skin and human foreskin was evaluated via a fl uorescence microscope Transdermal delivery of proteins mediated by non-covalently associated arginine-rich intracellular delivery peptides Arginine-rich intracellular delivery (AID) peptides Protein Transdermal delivery assay on mice (histological examination) (83) Protein internalization on human A549 cells(confocal s microscope) Cytotoxicity in Human A549 cells (MTT assay) A peptide carrier for the delivery of elastin into fi broblast cells Amphipathic cell– penetrating peptide carrier Elastin The SDS-PAGE technique was used to determine protein/peptide complex formation (85) Particle size distribution by DLS Particles morphology was determined via SEM. Cytotoxicity study in NIH-3T3tcells (MTT assay) Internalization of the complex in NIH-3T3 cells was evaluated using a fl uorescent microscope CoQ10enhances dermal elastin expression, inhibits IL-1α production and melanin synthesis in vitro O/W Nano emulsion CoQ10(CoQ 10 ) Investigation of CoQ10anti-aging effect in multiple adult fi broblast cell lines was performed by using a cell proliferation assay. (99) Illustrating the effect of CoQ10on ROSproduction u by radiating fi broblast cell lines with UV radiation followed by measuring the intracellular ROS level Evaluating the depigmentation potential of CoQ10was detected via melanin assay, tyrosinase activity measurement and DOPAvstaining Systematically optimized CoQ10- loaded proniosomal formulation for treatment of photo-induced aging in mice: characterization, biocompatibility studies, biochemical estimations and anti-aging evaluation Proniosomal gel formulation CoQ10 In vitro characterization of the proniosomal gel: (100) The % drug entrapped was determined by using HPLC method Particle size analysis was measured by using a Malvern zetasizer Morphological studies were detected by using TEM Rheological studies were determined by using a cup-and-bob viscometer. Ex vivo evaluation of the drug permeation and retention was performed. In vivo evaluation of the drug antiaging effect in female Swiss albino mice after exposure to UV radiation was carried out via visual, histopathological and other evaluations Supplementary table I Continued SKIN-AGING AND INFLAMMAGING TREATMENT 347
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. Current formulation and evaluation of a Q10-loaded SLN cream: in vitro and in vivo studies SLNs–loaded cream CoQ10 Particle size analysis and zeta potential measurement of SLNswere w detected by using photon correlation spectroscopy (107) Drug–excipient compatibility was determined by differential scanning calorimetry Visualization of the colloidal dispersion was performed by TEM In vitro release study was conducted by using an automated, temperature-controlled continuous fl ow diffusion cells. In vivo antiaging capabilities of developed formulation were evaluated in 25 female volunteers by assessment of skin hydration and viscoelasticity The advantages of a CoQ10 delivery system in skin photo- protection NLCs CoQ10 Particle size and shape of NLCs were determined via Zetasizer and TEM, respectively (108) Cell viability testing was detected by using Human embryo skin fi broblasts via MTT assa Antioxidant assessment through lipid peroxidation products and intracellular ROS assays was performed by using the photometrical method Biochemical evaluation of the antioxidant parameters and enzymes activity Cell apoptosis was determined by fl uorescence microscopy In vivo skin permeation was conducted by using female Sprague– Dawley rats via fl uorescent microscopy TRF attenuates UV-induced infl ammaging: A bench to bedside study Nanoemulsion TRF In vitro studies: (52) Determination of cell viability in HaCatcell x line using MTT assay Quantifi cation of certain oxidative and infl ammatory markers in HaCat cell line after UVB exposure using the ELISA technique. ROS measurement by fl ow cytometry and fl uorescence plate reader Ex vivo studies to investigate the drug permeability and a antioxidant effect were conducted by the skin antioxidative potential method and radical sun protection factor test using skin samples from the external lobe of a fresh pig ear Clinical studies on healthy human volunteers involving UV irradiation and skin color measurements were carried out Supplementary table I Continued JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 348
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)