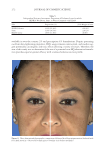
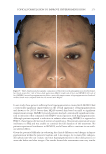
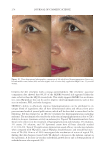
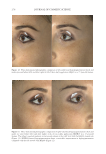
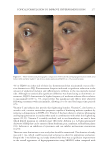
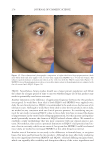
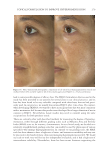
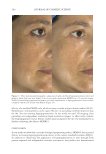
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. Anti-infl ammaging and antiglycation activity of a botanical ingredient from African biodiversity (Centevita™) Conventional (solution) Extract from Madagascar, and Centella asiatica Biological activity on human skin explants through determination of several parameters: (142) Thymine photodimerization induced by UV Interleukin (IL)1-α, ROS scavenging properties Antiglycation activity Antiwrinkle effect was evaluated via a clinical trial on healthy volunteers and skin parameters such as skin replicas, fi rmness, elasticity and collagen density Topical vesicular formulations of Curcuma longa extract on recuperating the ultraviolet radiation–damaged skin Liposomes, ethosomes, and transfersomes in cream Curcuma longa extract Physicochemical characterizations of the vesicular systems including particle size analysis, TEM imaging, and entrapment effi ciency determination were conducted (103) Physicochemical evaluations of creams pH, viscosity, stickiness, smoothness, stability, spreadability and microbial count were carried out Clinical study on human volunteers was performed and skin hydration and sebum content were determined Functional response of bioprotective poloxamer-structured vesicles on infl amed skin Nanovesicles (liposomes and glycerosomes modifi ed by poloxamers) Resveratrol and gallic acid Vesicles size and shape were evaluated via photon correlation spectroscopy, and cryogenic transmission electron, respectively. (93) Viscosity measurement was performed by the cone-and-plate rheometer Stability studies In vitro skin permeation through Franz diffusion cells Drug deposition study was conducted using tape stripping to remove the stratum corneum followed by HPLC analysis of drug content Cell viability testing and protection against oxidative stress on mouse embryonic fi broblasts (3 T3) using MTT assay were evaluated In vivo antinfl ammatory effect was evaluated in female CD-1 mice through edema and myeloperoxidase inhibition Supplementary table I Continued SKIN-AGING AND INFLAMMAGING TREATMENT 349
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. An approach based on lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for topical delivery of α-Lipoic acid SLNs α-Lipoic acid Particle size was determined by photon correlation spectroscopy (143) Drug–excipient compatibility was evaluated by differential scanning calorimetry analysis Rheological analysis was performed by oscillation frequency sweep tests a Dynamic light scattering b Stratum corneum c High-performance liquid chromatography d Nanostructured lipid carriers e Scanning electron microscope f Transmission electron microscopy g Ferric reducing ability of plasma h ABTS i Ultraviolet B radiation j 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide k Matrix metalloproteinase-2 l Sodium dodecyl sulfate- polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis m Thin layer chromatography n Differential scanning calorimetry o Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy p Polydispersity index q Confocal laser scanning microscopy r Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay s Adenocarcinomic human alveolar basal epithelial cells t Fibroblast cell line u Reactive oxygen species v 3,4-Dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine w SLNs x Immortalized human keratinocyte cell line Supplementary table I Continued JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 350
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)