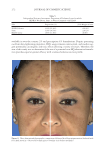
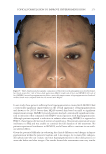
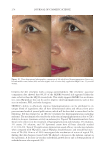
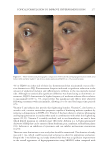
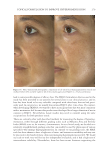
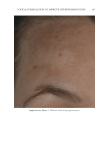
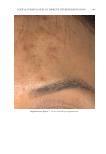
TOPICAL FORMULATION TO IMPROVE HYPERPIGMENTATION 267 PAT IENT SELF-ASSESSMENT Afte r 1 mo of treatment, the patients assessed the two products from baseline on overall appearance, irritation, redness, and tolerability using a Likert scale (Table I). One patient dropped out of the study after 2 wk because of severe irritation, redness, and intolerability from HQ4% use. This patient’s last observation for HQ4% was carried forward to the 1-mo assessment. Over all appearance. Aft er 1 mo of SKNB19 treatment, of the 18 patients, 18 (33.3%) saw a mild improvement, six (33.3%) patients saw a moderate improvement, and six (33.3%) patients saw a signifi cant improvement in the overall appearance of their hyperpigmenta- tion relative to baseline. After 1 mo of HQ4% treatment, of 18 patients, one (5.6%) saw worsening in overall appearance, three (16.7%) saw no change, 11 (61.1%) saw a mild improvement, and three (16.7%) saw a moderate improvement in their hyperpigmentation relative to baseline (Figure 1, Table III). Of the 18 patients, 15 (83.3%, Confi dence Interval (CI): 66.1–100%) rated the SKNB19-treated side as having better overall appearance than the HQ4%-treated side. Of the 18 patients, three (16.7%, CI: 0.0–33.9%) rated both the SKNB19- and HQ4%-treated sides as having the same overall appearance. None of the patients rated the HQ4%-treated side as having better overall appearance (Figure 2). Differences in pair-wise scores were statistically signifi cant (p = 0.001). After 1 mo of treatment, patients reported a 100% improvement (mild, moderate, or signifi cant) in the overall appearance of SKNB19-treated skin sections and 77.8% improvement in HQ4%- treated skin sections. Relative to HQ4%, this is a 28.5% improvement with SKNB19. Figure 1. Patient self-assessment: Distribution of overall appearance scores. Table II Independent Reviewer Assessment Scale Score -1 0 1 2 3 Overall appearance Worsened No change Mild improvement Moderate improvement Signifi cant improvement
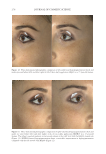
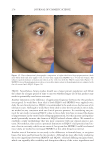
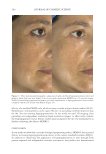
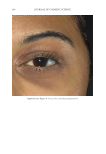
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 268 Irri tation. Aft er 1 mo, 100.0% of patients reported no irritation on the SKNB19-treated side. By contrast, of the 18 patients, 13 (72.2%) reported no irritation, four (22.2%) re- ported mild irritation, and one (5.6%) reported signifi cant irritation on the HQ4%- treated side (Figure 3). On pair-wise comparison, fi ve of the 18 (27.8%, CI: 7.1–48.5%) patients reported less irritation with the SKNB19-treated side, whereas none reported less irritation with the HQ4%-treated side. Differences in pair-wise scores were mildly statistically signifi cant (p = 0.048). Redn ess. Aft er 1 mo, of the 18 patients, 16 (88.9%) reported no redness and two (11.1%) reported mild, transient redness on the SKNB19-treated side, whereas 13 (72.2%) pa- tients reported no redness, three (16.7%) reported mild redness, one (5.6%) reported moderate redness, and one (5.6%) reported signifi cant redness on the HQ4%-treated side (Figure 4). On pair-wise comparison, of the 18 patients, fi ve (27.8%, CI: 7.1–48.5%) patients reported less redness with the SKNB19-treated side, whereas two (11.1%, CI: Table III Patient Self-Assessment: Distribution of Overall Appearance Scores Treatment Score Proportion (%), N = 18 patients 95% Margin of error SKNB19 Worsened 0 (0.0%) ±0.0% No change 0 (0.0%) ±0.0% Mild improvement 6 (33.3%) ±21.8% Moderate improvement 6 (33.3%) ±21.8% Signifi cant improvement 6 (33.3%) ±21.8% HQ4% Worsened 1 (5.6%) ±10.6% No change 3 (16.7%) ±17.2% Mild improvement 11 (61.1%) ±22.5% Moderate improvement 3 (16.7%) ±17.2% Signifi cant improvement 0 (0.0%) ±0.0% Figure 2. Patient self-assessment: Bar plot demonstrating the proportion of overall appearance scores for which SKNB19 was better, same, or worse compared with HQ4%. In 83.3% of cases, SKNB19 was rated as having better overall appearance than HQ4%. In 16.7% of cases, SKNB19 and HQ4% were rated as having the same overall appearance.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)