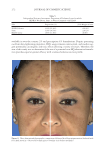
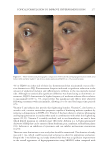
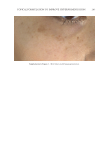
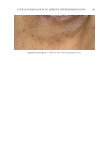
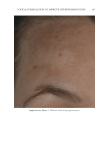
TOPICAL FORMULATION TO IMPROVE HYPERPIGMENTATION 275 EGF has been previously demonstrated to decrease infl ammation-induced melanogenesis. Melanocytes respond to EGF through the extracellular signal–regulated kinases, which serve to reduce melanin synthesis through downregulation of microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (27). EGF is also able to limit hyperpigmentation by reducing ty- rosinase activity and reducing melanogenesis (17). A recent randomized controlled study found that topical EGF improved melasma in their 15-patient cohort (28). There is increased interest in other growth factors that have been shown to improve pigmentation in animal models. For instance, TGF-β1 has been shown to reduce melanocytic activity in a rat model study. A recent topical product using TGF-β1 along with other ingredients has been shown to improve melasma (29). IL-6 shows promise as well by inducing depigmentation in a prior animal study by Choi et al (30). Last, Yamaguchi et al have extensively studied DKK1, which is an inhibitor of Wnt signaling. DKK1 has been shown to be expressed in high mRNA levels by fi - broblasts in the dermis of the human skin on the palms and soles and inhibits the function and proliferation of melanocytes in the palmoplantar epidermis (31,32). Although there is potential for DKK1’s targeted pathway in reducing pigmentation in the palmoplantar epidermis, future studies will need to further investigate DKK1’s role in hyperpigmentation. N iacinamide, also known as vitamin B3, is a water-soluble vitamin that has been shown to reduce melanosome transfer (33), provide photoprotection (34), and possess anti- infl ammatory properties (35–37), all of which can be attributed to its effi cacy in the treatment of hyperpigmentation. A double-blinded, left–right randomized clinical trial in which patients with melasma were randomly treated with either niacinamide Figure 11. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of right-sided facial hyperpigmentation (lower eye- lid and midface area) before (left) and after (right) 4 wk of twice-daily application SKNB19 in a 53-year-old woman. SKNB19-treated hyperpigmentation shows a noticeable improvement in hyperpigmentation com- pared with the side treated with HQ4% (Figure 10).
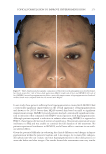
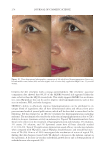
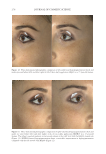
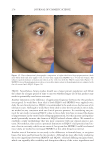
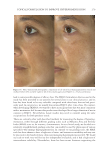
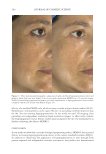
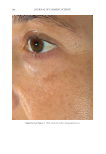
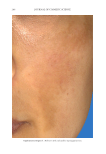
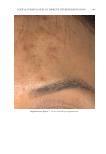
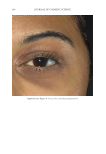
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 276 Figure 13. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of right-sided facial hyperpigmentation (cheek and under eye area) before (left) and after (right) 4 wk of twice-daily application SKNB19 in a 27-year-old woman. The subject reported moderate irritation and redness at the 4-wk visit with the HQ4%-treated side (Figure 12). SKNB19-treated hyperpigmentation shows a noticeable improvement in hyperpigmentation compared with the side treated with HQ4% (Figure 12). Figure 12. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of left-sided facial hyperpigmentation (cheek and under eye area) before (left) and after (right) 4 wk of twice-daily application HQ4% in a 27-year-old woman.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)