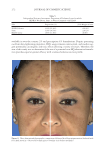
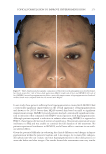
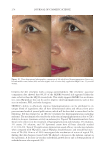
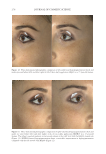
TOPICAL FORMULATION TO IMPROVE HYPERPIGMENTATION 271 On pai r-wise comparison, of the 85 SKNB19-treated cases, 31 (36.5%, CI: 26.3–46.7%) were rated as being equal in overall appearance by the independent evaluators compared with the HQ4%-treated cases, and 44 (51.8%, CI: 41.2–62.4%) were rated as having better overall appearance by the independent evaluators than the HQ4%-treated cases. Of 85 the HQ4%-treated cases, 10 (11.8%, CI: 5.0–18.6%) were rated as having a better overall appearance (Figure 7, Table V) than the SKNB19-treated cases. In summary, on pair-wise comparison, the independent reviewer assessment showed that evaluators gave higher scores to SKNB19-treated sides than HQ4%-treated sides (p 0.001). Most notably, 88.2% of the SKNB19-treated sides appeared to be equal to or better than the HQ4%-treated sides. Figures 8-17 present the before and after results of fi ve patients that were included in the study. DISCUS SION Hyperp igmentation is a dermatologic condition that causes an unappealing appearance in a variety of individuals. The current mainstay of treatment is topical HQ, which is Table IV Independent Reviewer Assessment: Distribution of Evaluator Scores for Overall Appearance Treatment Score Score counts (%), N = 85 95% Margin of error SKNB19 Worsened 2 (2.4%) ±3.2% No change 13 (15.3%) ±7.7% Mild improvement 31 (36.5%) ±10.2% Moderate improvement 26 (30.6%) ±9.8% Signifi cant improvement 13 (15.3%) ±7.7% HQ4% Worsened 4 (4.7%) ±4.5% No change 26 (30.6%) ±9.8% Mild improvement 32 (37.6%) ±10.3% Moderate improvement 22 (25.9%) ±9.3% Signifi cant improvement 1 (1.2%) ±2.3% Figure 7. Independent evaluator assessment: Bar plot showing proportion of evaluator scores for which SKNB19 was better, same, or worse compared with HQ4%.
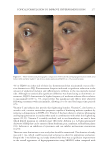
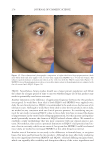
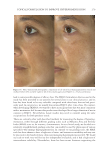
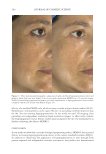
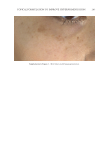
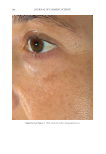
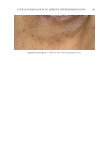
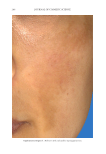
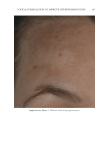
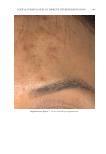
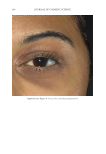
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 272 available in over-the-counter 2% and prescription 4% formulations. Despite possessing excellent skin-lightening properties, HQ’s usage remains controversial, and studies sug- gest potentially carcinogenic and toxic effects affecting a variety of tissues. Therefore, the aim of this study was to determine if the use of a potential non-HQ alternative formula- tion provides equal or greater effi cacy with a reduced adverse reaction profi le. Figure 8. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of bilateral facial hyperpigmentation (forehead/mid- face/cheek areas) in a 38-year-old woman prior at baseline visit (before treatment). Table V Independent Reviewer Assessment: Proportion of Evaluator Scores for which SKNB19 Was Better, Same, or Worse Compared with HQ4% Side Proportion (%) 95% Margin of error SKNB19 better 44/85 (51.8%) ±10.6% Same 31/85 (36.5%) ±10.2% HQ4% better 10/85 (11.8%) ±6.8%
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)