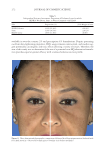
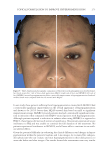
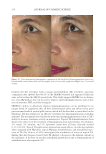
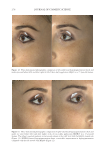
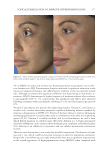
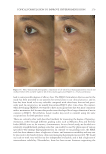
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. Development of herbal cosmetic cream with Curcuma longa extract–loaded transfersomes for antiwrinkle effect Transfersomal cream Curcumin from Curcuma longa extract In vitro characterization of curcumin containing transfersomes: (104)) Morphological examination of the vesicles using transmission electron microscopy (TEMf) Spectrophotometric determination of the entrapment effi ciency Particle size and zeta potential measurement by a Malvern Zetasizer Storage stability over 6 months In vitro skin permeation and deposition studies were carried out by using 2-stage modifi ed Franz diffusion cells. Characterization of curcumin incorporated transfersomal cream Physicochemical evaluation of the cream (color, odor, content, pH, acid, ash, and saponifi cation value) The irritation test on human volunteers was carried out with determination of the erythemal score established by the Indian standards In vivo studies were carried out on female human volunteers to evaluate the skin elasticity using a cutometer Topical formulation containing NGN: effi cacy against ultraviolet B irradiation-induced skin infl ammation and oxidative stress in mice Conventional topical formulations NGN In vitro evaluation of NGN antioxidant activity was performed by using FRAPg, ABTS, h hydroxyl, iron-dependent and iron independent lipid peroxidation tests (50) Physicochemical characterization of the developed topical formulations was detected In vivo evaluation of the effi cacy of the NGN containing topical formulations in sex matched hairless mice subjected to UVBi radiation of measured intensity was performed by using various measurements (skin edema, cytokine measurement, FRAP, ABTS, catalase assay, lipid peroxidation, superoxide anion production, glutathione assay and others) Supplementary table I Continued SKIN-AGING AND INFLAMMAGING TREATMENT 345
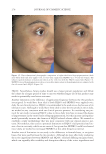
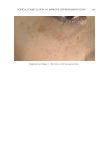
Title Formulation type Drug Evaluation Refs. In vitro and in vivo skin antiaging evaluation of gel containing niosomes loaded with a semi- purifi ed fraction containing gallic acid from Terminalia chebula galls Gel containing niosomes Semi-purifi ed fraction containing gallic acid In vitro biological antioxidant activity of gallic acid and the semi purifi ed fraction incorporated into the optimized elastic and non-elastic niosomes was estimated via the free-radical scavenging (96) Cytotoxicity assay was performed via MTTjassay MMP-2kinhibition activity by gelatinolytic zymography (gelatinolytic activities of MMP-2 was assessed by SDS-PAGEl zymography using gelatin as a substrate) Evaluating the physicochemical stability of the gel containing niosomes loaded with the semi-purifi ed fraction was carried out Skin irritation tests on male rabbits (irritation index depends on erythema and edema degree) Effi cacy investigation of the antiaging potential of the optimized gel in human volunteers was detected via determination of skin elasticity, surface microstructure, hydration, erythema and pigmentation Development and evaluation of vesicular system for curcumin delivery Phyto-vesicles, liposomes and niosomes Curcumin Characterization of curcumin–phosphatidyl choline complex was performed via TLCm, DSCn, melting point, and FTIRo (97) Characterization of the vesicular systems Morphological study by TEM Vesicles size and PDIp by Malvern Zetasizer Spectrophotometric determination of the entrapment effi ciency Assessment of the anti–aging capability of the developed vesicular systems in UV-radiated Swiss albino mice was carried out by examining certain biochemical markers, moisture content, and histological analysis Effects of skin penetration enhancers in topical antiaging products containing α-hydroxyacids and hyaluronic acid Conventional lotion α-Hydroxyacids Evaluating the effect of different permeation enhancers on transdermal penetration was performed by using skin permeation tests via diffusion cells (72) Hyaluronic acid Supplementary table I Continued JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 346
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)