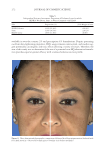
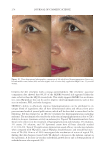
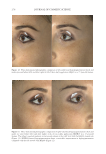
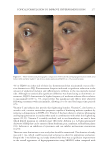
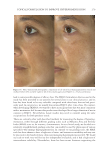
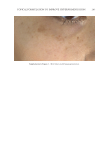
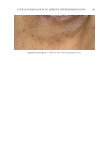
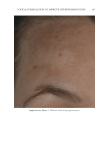
TOPICAL FORMULATION TO IMPROVE HYPERPIGMENTATION 279 lead to some possible degrees of effi cacy bias. The HQ4% formulation that we used in the study has been provided to our patients for several years in our clinical practice, and its base has been found to be very tolerable compared with other bases that we had previ- ously used. In our practice, we usually discontinue HQ4% after 1 mo of use. By contrast, when developing SKNB19, we wanted to have an excipient base that was more consistent with a moisturizer feel because this product was developed for a longer duration of use in contrast to HQ4%. Nevertheless, future studies may need to consider using the same excipient base for both products tested. T here are certainly other well-described methods for measuring the degree of hyperpig- mentation, either through different grading scales such as Melasma Area and Severity Index (MASI) score or, for instance, chromameters. In our clinical study, we decided on a relatively straightforward grading scale that can readily be used by physicians of various specialties who manage hyperpigmentation. In contrast to our grading scale, the MASI scale has been shown to have a high rate of intra- and interrater variability and may not be practical in the hands of many clinicians managing hyperpigmentation (40). We found our scale to work very well for our fi ve independent evaluators, and it had a high rate of interevaluator reliability. Nevertheless, there has been recent literature supporting the Figure 16. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of left-sided facial hyperpigmentation (cheek and midface) before (left) and after (right) 4 wk of twice-daily application HQ4% in a 53-year-old woman.
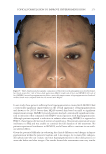
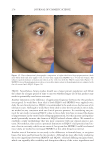
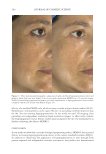
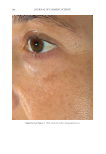
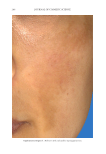
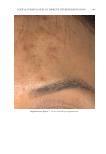
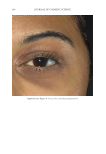
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 280 effi cacy of a modifi ed MASI scale, which we may consider using in future studies (40,41). Furthermore, chromameters can be quite effective in providing excellent objective data for the clinician treating hyperpigmentation. In our study, we used 3D imaging, thus providing our independent evaluators high-resolution images to effectively evaluate the hyperpigmented areas. Future studies may incorporate the use of a chromometer in further evaluating the effi cacy SKNB19. C ONCLUSION I n our study, we show that a recently developed proprietary product, SKNB19, has increased effi cacy in treating hyperpigmentation relative to the current standard treatment HQ4%. In addition to improving the appearance of hyperpigmentation as seen through both patient-reported and independent reviewer assessments, the product also demonstrated Figure 17. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of right-sided facial hyperpigmentation (cheek and midface) before (left) and after (right) 4 wk of twice-daily application SKNB19 in a 53-year-old woman. SKNB19-treated hyperpigmentation shows a noticeable improvement in hyperpigmentation more so when compared with the side treated with HQ4% (Figure 16).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)