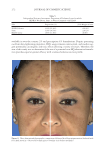
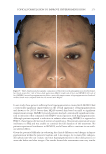
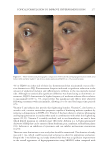
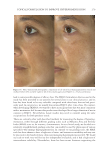
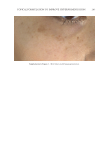
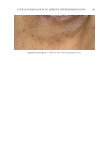
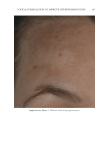
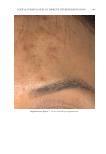
TOPICAL FORMULATION TO IMPROVE HYPERPIGMENTATION 273 In our study, those patients suffering from hyperpigmentation treated with SKNB19 had a statistically signifi cant improvement in the overall appearance of hyperpigmentation and shown to be 28.5% better than HQ4%-treated skin based on mild to signifi cant improvement ratings. SKNB19-treated patients also had a statistically signifi cant reduc- tion in irritation when compared with HQ4%-treated patients with hyperpigmentation. Although patients reported a reduction in redness when using SKNB19 as opposed to HQ4%, these fi gures did not reach statistical signifi cance. One patient experienced severe intolerance to HQ and was unable to continue the full duration of the treatment. No patients experienced intolerance to SKNB19, and all were able to continue its use with- out adverse effects. Given the potential diffi culty in evaluating the clinical differences and changes in hyper- pigmentation within the patient’s baseline and 1-mo images, we recruited fi ve indepen- dent physicians who can evaluate and treat hyperpigmentation in their daily practice to assess the before and after images. Our results showed the assessments were very similar Figure 9. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of bilateral facial hyperpigmentation (forehead/mid- face/cheek areas) after 4 wk of twice-daily application HQ4% (right side of face) and SKNB19 (left side of face) SKNB19-treated hyperpigmentation shows a noticeable improvement in hyperpigmentation (forehead/ midface/cheek area) compared with the side treated with HQ4%.
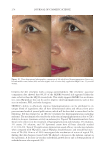
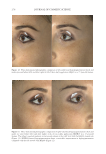
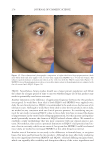
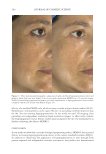
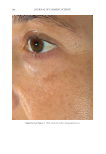
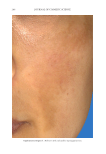
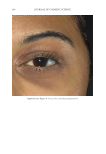
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 274 between the fi ve reviewers with a strong interreliability. The reviewers’ pair-wise comparison data showed that 88.2% of the SKNB19-treated side appeared either the same or better than the HQ4%-treated side. This study supports SKNB19 as an alterna- tive, non-HQ product that can be used to improve skin hyperpigmentation, such as that seen in melasma, PIH, and solar lentigines. SKNB19 ’s ability to effectively improve hyperpigmentation can be attributed to its unique blend of ingredients that all have demonstrated safety and effi cacy from prior peer-reviewed medical journal publications, which will be described in more detail in the following. TA has emerged as an effective treatment for hyperpigmentation including melasma. The mechanism of action for the reduction in hyperpigmentation is due to TA’s ability to decrease tyrosinase activity in melanocytes. Topical TA formulations have been shown to be effective in the treatment of hyperpigmentation and melasma 2% emulsion, 3% cream, 5% solution, and 5% liposomal cream have all been clinically studied (11,13,18–20). Topical TA applications demonstrate equal effi cacy in reducing melasma when compared with HQ alone, topical HQ plus dexamethasone, and intradermal injec- tions of TA (26). Kim et al 2016 investigated the mechanism of action of topical TA, fi nding that skin biopsies treated with TA showed a decrease in the melanin content in the epidermis. A decrease in vascular endothelial growth factor and a downregulation of endothelin were also reported (20). Figure 10. Three-dimensional photographic comparison of left-sided facial hyperpigmentation (lower eye- lid and midface area) before (left) and after (right) 4 wk of twice-daily application HQ4% in a 53-year-old woman.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)