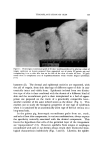
SUBCELLULAR COMPONENTS FROM HUMAN EPIDERMIS 103 Figure 5. Electron micrograph of a microsomal pellet prepared from human epidermis, showing ribosomes (X 80,000) derreal cells, the force necessary to disrupt these cells may well facilitate fragmentation, particularly in epidermis which is not fresh. The opti- mum pH of keratinase (8.0) used for the determination of the enzyme activity is rather close to that of tris buffer (7.6), used for the isolation of microsomes from rat liver (15) in which case there was no fragmentation. The cytochrome oxidase activity was low and relatively the same in mitochondrial fractions obtained from untreated and keratinase-treated epidermis. Electron micrographs of the mitochondrial pellets showed the presence of partially intact and fragmented mitochondria along with other particulate material (Fig. 6). This contamination, as well as frag- mentation of the mitochondria, would account for the low activity of cytochrome oxidase. Bagatell et al. (16) and Rosett et al. (17) have iso- lated mitochondria from fresh rat epidermis. These preparations were also heavily contaminated with other tissue components. Due to the presence of desmosomes, keratohyalin granules, and perhaps lysosomes and other particulate matter such as keratin, the isolation of pure mito- chondria from epidermis poses a considerable challenge. The very nature of epidermis, containing basal cells, differentiating cells in the process of keratinization, cells in the process of dying, as well as the granular and keratin layers, complicates the isolation of mitochondria in pure form.
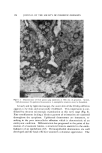
]04 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Figure 6. Electron micrograph of a mitochondrial pellet prepared from human epidermis showing some partially intact and some fragmented mitochondria, keratohyalin, and other particulate matter (X 53,000) Table III Synthesis of NAD by Nuclei from Human Epidermis Condition #Moles of NAD Synthesized/hr/mg Nitrogen" Epidermis, without keratinase Epidermis, treated 20 min with keratinase Epidermis, treated 30 rain with keratinase 1.45 q- 0.23 1.23 q-- 0.19 1.15 q- 0.18 Mean q- S.D. of 4 experiments. There appears to be no significant difference in the •nloles NAD synthesized per hr/mg nuclear nitrogen between the nuclei obtained from normal and keratinase-treated epidermis (Table III). DISCUSSION The use of enzymes has been advocated by some investigators for the preparation of cell particulates. The proteolytic enzyme, Nagarse, was used by Chance and Hagihara (2) in the preparation of mitochondria from muscle tissue, snail gut enzyme by Duell et al. (3) for the enzymic digestion of yeast cells, and trypsin by Weiss (18) for the relnoval of an
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)