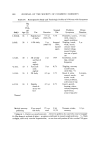
PPD AND RESORCINOL IN HAIR DYES 857 0.5 3•8 2 pH=8 400 500 600 700 Wavelength (millimicrons) Figure 4. Effect of pH on visible spectrum of green component from p-phenylenediamine and resorcinol oxidation Figure 5. Wavelength (microns) 3 4 5 6 7 8 10 20 1.o• 4000 3000 2000 1000 Frequency (cm -• ) Infrared spectrum of green component from p-phenylenediamine and resorcinol oxidation Infrared Spectrum The infrared spectrum (Fig. 5) was obtained using the KBr pellet technique. The absorption bands at 3420, 3330, and 3175 cm -• indi- cated the presence of amino groups. The phenolic hydroxyl could not be positively identified from the spectrum because the characteristic C-H and N-H stretching frequency bands are very strong in the 3600-2900 cm -• region. The strong absorption peak at 1630 cm -• was indicative of the quino- noid structure. Mass Spectroscopy The molecular weight of 320 for the component was determined by mass spectrometry. The even mass number confirms the presence of an even number of nitrogen atoms in the molecule (25). The fragmentation pattern was too complex to allow an accounting of all the species, but fragments such as aniline (m/e 93), phenol (m/e 94), phenylenediamine (m/e 108), and dihydroxybenzene (m/e 110) were clearly recognized (Fig. 6).
858 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS . 40 80 120 160 •0 320 200 ,•/, 2•o Figure 6. Mass spectrum of green component from p-phenylenediamine and resorcinol oxidation The methoxy derivative, obtained by treating the green component with diazomethane, had a molecular weight of 334 indicating the presence of only one hydroxyl group. A molecular weight of 348 was found for a ring dimethylated deriva- tive, obtained from 2,5-diaminotoluene and resorcinol, which confirms the proposed 2:1 ratio for phenylenediamine and resorcinol parent groups in the structure. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy The nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of the green component (Fig. 7) was obtained in deuterated methanol on a Model HA-100 instru- ment.* It showed three groups of protons. The doublets at 710 and 670 cps were assigned to the aromatic hydrogens designated HA and HB, respectively. The singlet at 608 cps designated He is assigned to the quinonoid protons on the central ring. The ratio of the areas of the three peaks corresponds to the relative concentrations for 2:2:1 for the three groups of protons. The labile protons of NH,. and OH groups readily exchange with the deuterium of the solvent (26). Therefore, the spectrum was superim- posed over a shoulder extending beyond the measured range due to the net effect of amino, hydroxyl, and solvent protons. The presence of a phenolic hydroxyl group in this component was reconfirmed by the appearance of a sharp peak at 316 cps corresponding * Varian Associates, Palo Alto, Calif.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)