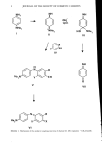
j. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 37, 1-8 (January/February 1986) The role of the primary intermediate, N, N-b is-( 2-hyd roxyethyl )-p-p h e nyl e ned ia m i n e in oxidative hair dyeing KEITH C. BROWN and JOHN F. CORBETT, Clairol Research Laboratories, 2 Blachley Road, Stamford, CT 06922. Received September 16, 1985. Synopsis The primary intermediate, N,N-bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)-p-phenylenediamine, reacts with standard couplers under oxidative conditions to give indo dyes following a mechanism similar to that previously established for p-phenylenediamine. However, under certain circumstances, the substituted diamine undergoes hydrol- ysis to p-benzoquinone monoimine which then reacts with the couplers to give a different series of indo dyes. Since indo dyes from the substituted diamine have visible absorption maxima at longer wavelengths than either those from the parent diamine or from the monoimine, hydrolysis will result in a significant color shift. In acid solution, indo dyes derived from the substituted diamine are more stable than analogous dyes from p-phenylenediamine, which accounts for the much improved wearing properties of these dyes. INTRODUCTION The kinetics and mechanism of coupling reactions of N,N-bis-(2-hydroxyethyl)-p- phenylenediamine (I), a common primary reactant in oxidative hair dye products, have recently been determined (1). In light of these results, it is now appropriate to discuss the role of this diamine in dye formulations. EXPERIMENTAL Spectrophotometric and kinetic techniques used in this work have been described pre- viously (1,2). All chemicals were commercial materials used without further purification. Indo dyes were generally prepared in situ by oxidizing equimolar proportions of the appropriate components with four equivalents of potassium ferricyanide or atmospheric oxygen. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION COUPLING REACTIONS The mechanism of oxidative dye-forming reactions of the substituted diamine I with typical couplers is shown in Scheme 1. This mechanism differs from those determined for coupling reactions with p-phenylenediamine or p-aminophenol because diimine II 1
2 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS NHe2 + INI He2 HO NHe III NH He:,N y" • •XH II o v vii He2N.• Vl Scheme 1. Mechanism of the oxidative coupling reactions of diamine (I). (He represents -CH2CH2OH).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)