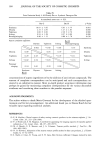
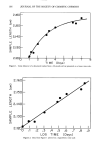
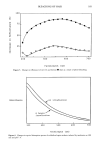
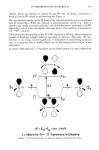
168 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS has been claimed to be responsible for the formation of defective collagen. These theo- ries are based on the assumption that mechanical response is associated with the forma- tion of crosslinks between collagen molecules. The observation reported here is that in the normal development of rat tail tendon there are not enough efj•ctive crosslinks synthesized to make significant contributions to the mechanical strengths of the tissues studied. Subsequent to the thermal denaturation of a rat tail tendon under mild conditions where it is reasonable to expect that only denatur- ation and not extensive hydrolytic scission has occurred, our mechanical tests show that tissues lack the development of equilibrium extension lengths. Rather, these samples show a normal rubbery flow behavior like that exhibited by uncrosslinked materials. Such behavior indicates that there are not even a minimum number of effictive crosslinks necessary to form a network. This behavior was observed at each age of tendon studied. Since these tendons had significant mechanical strengths prior to thermal denaturation, we must conclude that the crystalline structure of collagen is the significant contributor to mechanical strength of this material. REFERENCES (1) J. J. Butzow and G. L. Eichhorn, Physical chemical studies on the age changes in rat tail tendon collagen, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 154, 208-219, 1968. (2) F. Verzar, "Aging of the Collagen Fiber," in International Review of Connective Tissue Research, D. A. Hall, Ed. (Academic Press, New York, 1964), p. 244. (3) A. J. Bailey and V. C. Duance, Collagen in acquired connective tissue diseases: An active or passive role? European Journal of Clinical Investigation, 10, 1- 3, 1980. (4) P. H. Byers, R. C. Siegel, K. A. Holbrook, A. S. Narayan, P. Bornstein, and J. G. Hall, Defective crosslink formation in collagen due to decreased lysyl oxidase activity, New England Journal of Medi- cine, 303, 61-65, 1980. (5) K. Chang, J. Uitto, E. A. Rowold, G. A. Grant, C. Kilo, and J. R. Williamson, Increased collagen cross-linkages in experimental diabetes, Diabetes, 29, 778-781, 1980. (6) L. E. Glynn, "Diseases of Collagen and Related Tissues," in International Review of Connective Tissue Research, D. A. Hall, Ed. (Academic Press, New York, 1964), pp. 238-244. (7) M. E. Nimni, A defect in the intramolecular and intermolecular cross-linking of collagen caused by penicillamine, J. Bio. Chem., 243, 1457-1467, 1968. (8) F. M. Sinex, "The Role of Collagen in Aging," in Treatise on Collagen, B. S. Gould, Ed. (Academic Press, New York, 1968), p. 439. (9) M. J. C. Crabbe and J. J. Harding, Collagen crosslinking: Isolation of two crosslinked peptides in- volving 2-CB (3-5) from bovine scleral collagen, FEBS Letters, 97, 189-192, 1979. (10) N. D. Light, Bovine type I collagen. A study of crosslinking in various mature tissues, Blochim. Biophys. Acta, 581, 96-105, 1979. (11) D. J. Prockop, K. I. Kivirikko, L. Tuderman, and N. A. Guzman, The biosynthesis ofcollagen and its disorders, New England Journal of Medicine, 301, 77-83, 1979. (12) A. J. Bailey, S. P. Robins, and G. Balian, Biological significance of the intermolecular crosslinks of collagen, Nature, 251, 105- 109, 1974. (13) F. Bartos and L. Miroslav, Collagen, elastin and desmosines in three layers of bovine aortas of different ages, Exp. Geront., 14, 21-26, 1979. (14) O. O. Blumenfeld and P. M. Gallop, Amino aldehydes in tropocollagen: The nature a probable cross-link. Proc. N.A.S., 56, 1260-1268, 1966. (15) P. Bornstein and K. A. Piez, The nature of the intramolecular cross-links in collagen. The separation and characterization of peptides from the cross-link region of rat skin collagen, Biochemistry, 5, 3460-3472, 1966. (16) A.D. Deshmukh and M. E. Nimni, In vitro formation of intramolecular crosslinks in tropocollagen, Blochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 35, 845-853, 1969.
CROSSLINKING IN COLLAGEN i69 (17) (18) (19) (20) (21) (22) (23) (24) M. Fukae and G. L. Mechanic, Maturation of collageneous tissue, J. Bio. Chem., 255, 6511-6518, 1980. N. D. Light and J. Bailey, The chemistry of the collagen cross-links, Blochem. J., 185, 373-381, 1980. N. D. Light and J. Bailey, Polymeric C-terminal cross-linked material from type-1 collagen, Biochem. J., 189, 111-124, 1980. P.J. Flory, Principles of Polymer Chemistry (Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York, 1953), Chapter 11. A. B. Furtek, Application of Rubber Elasticity Theory to Crosslinked Denatured Collagen, Ph.D. disserta- tion, University of Southern California, 1974. P. D. Ritchie, Plasticisers, Stabilisers, and Fillers (The Plastics Institute, Iliffe Books Ltd., London, 1972). D. G. Kaplan, Studies on the Viscoelastic Behavior of Connective Tissue, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Southern California, 1972. D. Puett, A. Ciferri, and L. V. Rajagh, Interaction between proteins and salt solutions. II. Elasticity of collagen tendons, Biopolymers, 3, 439-459, 1965.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)