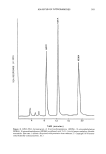
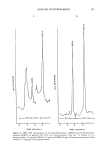
292 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table VII Representative List of Compounds Found to Give No Interference on the TEA Acetic acid Ethyl carbamate Oxalic acid Acetone Ethylene glycol n-Pentane Acetonitrile Fluorobenzene Phenylhydrazine Alizarin red Gasoline d,l-Phenylalanine Ammonia (gas) Glycerol p-Phenylazoaniline Benzene d-Glucose Phosphoric acid Benzyl salicylate Glutamic acid Propane 2-Butoxyethanol n-Hexane Pyridine Carbon dioxide Hydrogen Quinine Carbon disulfide Hydroquinone Sodium acetazolamide Carbon monoxide 8-Hydroxyquinoline Sulfadiazine Carbon tetrachloride Inosine Sulfanilic acid Chloral hydrate d,l-Isoleucine Tetrahydrofuran Chlorobenzene Methane (gas) Theophylline 1-Chloropropane Methyl acetate Toluene 2-Chloropropane N-Methyl bisacrylamide 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol Cyclohexane 2-Methylbutane 2,2,4-Trimethylpentane Cyclopentane Methyl formamide d,l-Tryptophan 1,2-Dichloroethane Methyl isobutyl ketone Urea 2,3-Dichloropropane Methyl orange Uric acid Diethyl ether Methyl red Urethane Dimethylamine Naphthalene Water p-Dioxane Nitrogen Xylene Diphenylamine Nitrobenzene Ethyl acetate o-Nitrotoluene See reference 20. range of sample types. Although the applications discussed here pertain to cosmetic finished product and raw material matrices, much of the developmental work had been done previously in such areas as the analysis of volatile N-nitroso compounds in food- stuffs. GC-TEA APPLICATIONS FOR VOLATILE NITROSAMINES The GC-TEA is the system of choice for the determination of volatile nitrosamines. This is exemplified by the quantity of literature available for the analysis of volatile nitrosamines in food products (Tables VIII and IX). Although volatile nitrosamines occur less frequently in cosmetic finished product and raw material matrices, gas chro- matographic separation of various volatile nitrosamines has also been reported (22,25- 27). Table X summarizes this data. The chromatogram of various volatile nitrosamines is presented in Figure 4. The lower molecular weight nitrosamines such as N-nitroso- dimethylamine, N-nitrosodiethylamine, and N-nitrosodipropylamine are relatively well resolved in comparison with the higher molecular weight nitrosamines, which show partial co-elution. In order to optimize the resolution of the nitrosamines being chromatographed, the chemical structure of the nitrosamine, the polarity of the column, column length and diameter, as well as the flow rate of the particular carrier gas, are important variables which must be considered. An example of how nitramines (recall that nitramines elicit TEA responses) may pose as potential interferents is shown
ANALYSIS OF NITROSAMINES 293 Table VIII Summary of GC Methods for Volatile Nitrosamine Analysis Method (detection limit) Sample type References GC-TEA a Foodstuffs 2, 37, 39, 46, 65, 68, 71, 75, 87, 89, 106, (0.1 to 5 ppb) 138, 139, 155, 174, 176, 184, 185, 190, 202, 223, 224, 227, 229, 232, 235, 236, 240, 251, 252, 264, 290, 310 Animal feed & grain 186, 228 Air 86, 102, 163 Water 90, 102, 158, 165, 239 Soil 243 Physiological specimens 38, 41, 107, 204, 208, 226, 230, 238, 285 Blood collection tubes 40 Commercial drugs 104, 212, 146, 283, 284 Tobacco products 151, 169, 178, 180, 195, 222, 233 Rubber products 215 Leather products 69 Baby bottle nipples 92, 110, 201, 209, 214, 282, 308 Cutting fluids 177 Cosmetics & raw materials 25, 26, 28, 29, 30, 44, 76, 95, 177 Miscellaneous 27, 47, 84, 153, 164, 194, 213, 216, 218, 225, 242, 248 GC-MS b Foodstuffs 46, 77, 87, 103, 123, 127, 154, 166, 183, (1 to 5 ppb) 231, 237, 241, 244, 247, 262, 267, 280, 309 Air 82, 128, 163, 211, 280, 287 Water 82, 148, 160, 165, 239, 280 Physiological specimens 280 Commercial drugs 280 Tobacco products 200, 280 Pesticides 124 Industrial chemicals 76, 280 Baby bottle nipples 20, 110, 201 Cosmetics 306 Miscellaneous 35, 59, 164, 171, 206, 249, 253, 254, 268 GC-FID' Quats 94 (ppb range) Air 157 Water 134, 144 Tobacco products 109 Miscellaneous 164, 175, 205, 245, 250 GC-AFID d Foodstuffs 46, 103, 183, 267 (ppb range) Air 82 Water 82, 162, 165 Miscellaneous 255, 266 GC-NPD e Industrial chemicals 76 (ppb range) Alkanolamines 292 Commercial drugs 269 GC-ECD f Foodstuffs 103, 120, 135, 150, 190, 256, 271 (1 to 50 ppb) Water 134, 144 Physiological specimens 208, 285 Cosmetics 45, 58 GC-CECD g Foodstuffs 36, 87, 103, 270 (ppb range) Air and water 82 GC-HECD • Foodstuffs 258 (ppb range) Water 165 (continued)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)