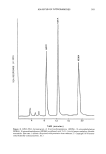
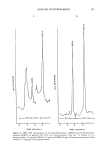
294 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table VIII (continued) Method (detection limit) Sample type References GC-PID i Cosmetics 305 ( 1 ppb) Foodstuffs 130 TEA, Thermal energy analyzer. MS, Mass spectrometer. FID, Flame ionization detector. AFID, Alkali flame ionization detector. NPD, Nitrogen-phosphorus detector. ECD, Electron capture detector. CECD, Coulson electrolytic conductivity detector. HECD, Hall electrolytic conductivity detector. PID, Photoionization detector. in Figure 5. The co-elution of these compounds along with some nitrosamine species can also be seen. The chromatograms shown in Figures 6 and 7 describe applications of GC-TEA for finished product analysis. Characteristic of both chromatograms are extraneous peaks that elute prior to the nitrosamine components. These components are a contribution from other materials in the sample matrix. The relatively "noisy" baseline is also due to matrix interferences and to the extremely high sensitivity required for these analyses. GC-TEA APPLICATIONS FOR NONVOLATILE NITROSAMINES The majority of the nitrosamines that occur in cosmetic finished products and raw materials are thermally labile. This is particularly true of the most commonly occurring species, N-nitrosodiethanolamine. Therefore, direct gas chromatographic analyses are difficult unless they are converted to volatile compounds. Since N-nitrosodiethanola- mine contains [3-hydroxyl groups, it can be derivatized to volatile species by a number of different chemical derivatization reactions. Acylation of the hydroxyl groups with acetic anhydride yields the corresponding acyl derivative: O O 2 CH3COCCH 3 + HOCH2CH 2 CH3CO2CH 2CH 2 \ \ NNO---) NNO + 2 CH3CO2H / / HOCH2CH2 CH3CO2CH2CH 2 (14) Reaction with MBTFA (N-methylbistrifluoroacetamide) yields the corresponding tri- fluoroacetyl compound: O O HOCH2CH 2 CF3CO2CH2CH 2 CF3C•qCCF 3 q- NNO ---) NNO / / CH 3 HOCH2CH2 CF3CO2CH2CH 2 + CH3NH2 (15) Trimethylsilylation of the hydroxyl groups is accomplished by reaction with MSTFA (N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltrifluoroacetamide):
ANALYSIS OF NITROSAMINES 295 0 •H 3 HOCH2CH 2 2 CF 3 - C - N - Si(CH3) 3 + NNO -- HOCH2CH2 / (CH3)3SiOCH2CH2 O NNO + 2 CF3CNHCH 3 (CH3)3SiOCH2CH 2 / (16) Table IX Summary of HPLC Methods for Nitrosamine Analysis Method (detection limit) Sample type References HPLC-TEA a (1 to 50 ppb) HPLC-MS b (1 to 5 ppb) HPLC-UV/Vis c (1 to 200 ppb) HPLC-PD a (ppb range) HPLC-PCD e (0.3 to 75 ppb) HPLC-EC f HPLC-FD g (ppb range) Foodstuffs Air Water Physiological specimens Tobacco products Rubber products Automobiles Leather products Industrial chemicals Cutting fluids Cosmetics & raw materials Blood collection tubes Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Air Water Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Cutting fluids Cosmetics & raw materials Miscellaneous Physiological specimens Metal-working fluids Cosmetics & raw materials Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Water Ethanolamines Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Miscellaneous Water Miscellaneous 115, 161, 192, 219, 220, 221, 224, 234 101 91 141 129, 179, 181 215, 307 67 69 136 111 1, 16, 42, 43, 48-54, 57, 62, 108 40 47, 196, 199 127 101 91 198 115 111 34, 55, 56, 60, 61, 74, 99, 137, 274, 306 140, 142, 182, 245 80, 141, 204 64 96, 275 73, 170 189 193 63 146 289 97, 291 193 207, 288 TEA, Thermal energy analyzer. MS, Mass spectrometer. UV/Vis, Ultraviolet/visible detection. PD, Polarographic detection. PCD, Photoconductivity detection. EC, Electrochemical detection. FD, Fluorescence detection.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)