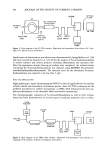
296 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS GC CARRIER GAS INJECTION HE ATED PTFE TUBE PORT 250øC TEA CATALYTIC PYROLYZER OZONE -80øC -150øC COLD TRAPS I VACUUM PUMP OPTICAL FILTER PM TUBE Figure 2. Flow diagram of the GC-TEA interface. (Reprinted with permission from reference 84. Copy- right 1975 Elsevier Science Publishers.) Applications of derivatization procedures were demonstrated by Spiegelhalder et al. (28) and more recently by Sommer et al. (29,30) for the analysis of N-nitrosodiethanolamine in several cosmetic and toiletry products including alkanolamine raw materials (30). After the appropriate sample clean-up procedures were completed, the isolated residue containing the N-nitrosodiethanolamine was silylated using MSHFBA (N-methyl-N- trimethylsilylheptafluorobutyramide). The detection limit for the derivatized N-nitroso- diethanolamine was reported to be less than 5 ppb. HPLC-TEA APPLICATIONS High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is directly applicable for the analysis of both volatile and nonvolatile nitrosamine species. Since GC-TEA techniques are the preferred procedures for volatile nitrosamines, so HPLC-TEA techniques have been ap- plied predominantly to the thermally labile nonvolatile nitrosamines. The chromatographic separation of N-nitrosodiethanolamine as well as other nitrosa- mines has been demonstrated on several types of packing materials such as silica, LIQUID INJECTION POnT ••r• CARnlERF..r'{ILTFOZOtlETEA•ICATALYTICPYnOLIZ[RHEAIoeOGAS .Pt_c COLUMN øfiOeC - 150'C COLD TRAPS Figure 3. Flow diagram of the HPLCoTEA interface. (Reprinted with permission from reference 27. Copyright 1978 Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association.)
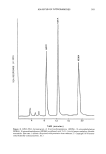
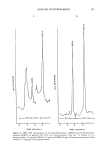
ANALYSIS OF NITROSAMINES 297 Table X GC-TEA Analysis of Nitrosamines Column type (length) Nitrosamine type a Reference 10% UCW-982 on Gas Chrom Q 80/100 NMODA, NMTA 25 (12ft x 2mm) 3% OV-101 on Gas Chrom 100/120 26 (10ft x 2mm) 3% Dexsil 300 on Chromosorb W AW 26 80/100 (12 ft x 2 mm) 15% FFAP on Chromosorb W 22 (2 m x 0.25 in) 10% Carbowax 20 M + 0.5% KOH on Chromosorb W/HP 80/100 (14ft X V, in) 6% OV-275 on Chromosorb WHP 80/100 (120 cm X 2.2 mm) 20% PEG-6000 (1 m X 3 mm) 15% DEGS (1 m X 3 mm) 1% XE-60 (1.5 m X 3 mm) 3% OV-17 (2 m x 3 mm) 15% SE-30 (3 m X 3 mm) 1% XE-60 (1.5 m X 3 mm) 0.5%EGA(1.5 m x 3mm) 3% OV-17 (2 rn x 3 mm) 15% SE-30 (3 rn X 3 mm) 20% PEG-6000 (1 m X 3 mm) 15% DEGS (1 m X 3 mm) 1% EDA (1.5 rn X 3 mm) 3% OV-17 (2 m X 3 mm) 15% SE-30 (3 m X 3 mm) NMODA NMODA NDMA, NDEA, NDiPA, NMPA, NDBA, NPip, NPyr, and their corresponding nitramines NDMA, NDEA, NDPA, NPip, NPyr, NMor 27 NDELA b 28, 29 o-Acyl derivatives c 59 o-Acyl derivatives c 59 o-Acyl derivatives c 59 o-Acyl derivatives c 59 o-Acyl derivatives c 59 o-Trifluoroacyl derivatives a 59 o-Trifluoroacyl derivatives d 59 o-Trifluoroacyl derivatives a 59 o-Trifluoroacyl derivatives a 59 o-Methyl ether derivatives e 59 o-Methyl ether derivatives e 59 o-Methyl ether derivatives e 59 o-Methyl ether derivatives e 59 o-Methyl ether derivatives e 59 a Nitrosamine type: NDMA, N-nitrosodimethylamine NDEA, N-nitrosodiethylamine NMPA, N-nitro- somethylpentylamine NDPA, N-nitrosodipropylamine NDBA, N-nitrosodibutylamine NDiPA, N-ni- trosodiisopropanolamine NMODA, N-nitrosomethyloctadecylamine NMTA, N-nitrosomethyltetradecy- lamine NPip, N-nitrosopiperidine NPyr, N-nitrosopyrrolidine NMor, N-nitrosomorpholine NDELA, N-nitrosodiethanolamine. b NDELA, bis-trimethylsilyl derivative of N-nitrosodiethanolamine from MSHFBA (N-methyl-N-tri- methylsilylheptafluorobutyramide). c,a,e Corresponding derivatives of hydroxylated nitrosamines including N-nitrosodiethanolamine. amino, cyano, and octadecylsilane-bonded phases (Table XI). For polar nitrosamines such as N-nitrosodiethanolamine, bonded phases that are slightly less polar than silica (such as the amino or cyano phases) are preferred since these phases tend to reduce tailing of the polar compounds (27). The overall optimization of both the chromato- graphic separation of the compounds of interest and the TEA response involves the proper choice of column and mobile phase. Chromatograms of standard nitrosamine mixtures, analyzed under different operating conditions, are shown in Figures 8 and 9. Figure 8 represents an example of volatile nitrosamines of low polarity chromatographed on a polar column (silica), while Figure 9 shows the polar nitrosamine, N-nitrosodiethanolamine, chromatographed on a less polar column (an amino-bonded phase). Characteristic in both chromatograms is the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)