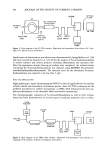
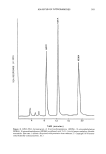
ANALYSIS OF NITROSAMINES 313 B Figure 20a. HPLC-UV chromatograms of N-nitrosodiethanolamine (NDELA) in lauramide DEA on Spherisorb ODS with 2:98 (v/v) methanol-water, adjusted to pH 4 with acetic acid. Flow rate: 1 ml/min. Detection: 254 nm at 0.005 AUFS. A: 333 ng NDELA. B: Lauramide DEA. (Reprinted with permission from reference 56. Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association.) NDELA Figure 2Oh. HPLC-UV chromatograms of N-nitrosodiethanolamine (NDELA) in lauramide DEA on Spherisorb ODS with 2:98 (v/v) methanol-water, adjusted to pH 4 with acetic acid. Flow rate: 1 ml/min. Detection: 254 nm at 0.005 AUFS. C: Lauramide DEA. D: Lauramide DEA + 500 ng NDELA. (Re- printed with permission from reference 56, Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association.)
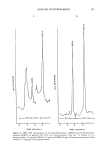
314 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS N ! I INJ INJ 2 4 • N z N D i ! • I INJ 2 4 INJ 4 Figure 21. HPLC-UV chromatograms of N-nitrosodiethanolamine (NDELA) in triethanolamine on Spherisorb ODS with 2:98 (v/v) methanol-water. Flow rate: 1 ml/min. Detection: 254 nm at 0.002 AUFS (N indicates NDELA peak). A: 775 ng NDELA. B: 85% Triethanolamine. C: 99% Triethanolamine. D: 99% Triethanolamine q- 775 ng NDELA. (Reprinted with permission from reference 55, Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association.) determination of nitric oxide using the nitric oxide analyzer (33). Any sample eliciting a positive response is reanalyzed using a standard GC-TEA or HPLC-TEA method to verify the specific nitrosamine compound or compounds present. Ultimate structural confirmation is done by mass spectrometry. The principle involved with this procedure is the chemical denitrosation of the nitrosa- mines with a solution of hydrobromic acid/acetic acid (or sodium iodide in the presence of acetic and sulfuric acids for aqueous matrices). The nitric oxide (NO) that is released through denitrosation is swept from the reaction mixture through the nitric oxide ana- lyzer. The resulting integrator response is proportional to the total nitrosamine content. Sample preparation involves the initial pretreatment of the sample with ammonium sulfamate and water followed by consecutive methylene chloride extractions. The re- sidual water is removed from the combined methylene chloride extracts with anhydrous sodium sulfate (this fraction contains the non-polar nitrosamines). The aqueous fraction (containing the polar nitrosamines) is adjusted to a pH of 3.5 and passed through a cation-exchange column to remove nitrates (nitrates cause peak broadening when ana- lyzed with the nitric oxide analyzer). Both fractions are then treated with denitrosating reagent and analyzed with the nitric oxide analyzer. Current concerns over this method- ology center around potential artifact formation during sample preparation.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)