ESTERIFICATION OF HYDROXY COMPOUNDS 249 GUERBET ALCOHOLS (9) Guerbet alcohols have been known since 1890 when Marcel Guerbet (10) first synthe- sized these materials. A typical reaction is represented by equation 2: Catalyst 2 CH 3 - (CH2) 8 - CH2OH -• CH 3 - (CH2)9•HCH2OH (2) CH 3 - (CH2) 7 Decanol is subjected to a modified aldol reaction and condenses to form a branched primary alcohol. We chose these materials to see if a high-purity primary alcohol that is beta-branched slows the rate of reaction due to steric factors. Specifically, we chose 2-octyl-dodecanol produced for these studies by Nova Molecular Technologies. The citrate ester of this material is the subject of a recent patent (11). POLYOXYALKYLENE GLYCOL COMPOUNDS Polyoxyethylene glycol 3350. This material was provided by Ethox Chemical, Greenville SC. The structure is HO-(CH2CH2-O)a-H. "a" is approximately 76. Polyoxypropylene glycol 4000. This material was provided by Ethox Chemical, Greenville, SC. The structure is HO-(CH2CH2-O)b-H. "b" is approximately 67. Methyl capped polyoxyethylene glycol. This material was provided by Ethox Chemical, Greenville, SC. The structure is CH3-(CH2CH(CH3)-O)c-H. "c" is approximately 7. SECONDARY ALCOHOL HO - ( - CH - CH 2 - O - )d -- H CH 3 Product Approx. "d" PPG 1000 14 PPG 2OOO 33 PPG 4OOO 67 HYDROXY SILICONE COMPOUNDS Dimethiconol compounds. Dimethiconol compounds are also referred to as silanol com- pounds, and conform to the following structure: •e• •el •4e HO •i•- O• •i•- O• SI-- OH (3) Me 1_ Me _[ Me e
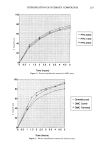
250 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS "e" is approximately 25. The product chosen for evaluation was provided by Siltech Inc., Norcross, GA. Dimethicone copolyol compounds (comb). The structure is as follows: Me• •i---[- 0• •i---• 0• •i•- 0--- Si--Me Me L. Me_] I R"_] Me f g (4) R" is-(CH2)3-O--(CH2CH2-O)7-H , 'T' is approximately 29, and "g" is approximately 4. The product chosen for evaluation was provided by Siltech Inc., Norcross, GA. Dimethicone copolyol compounds (terminal). The structure is shown below: •e [ Me O• Si-- R" Me L_ Me_l Me h (5) R" is -(CH2)3-O-(CH2CH2-O)7-H and "h" is approximately 29. The product chosen for evaluation was provided by Siltech Inc., Norcross, GA. EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURE In a suitable reaction vessel are added 1 mole of stearic acid and one mole equivalent of the hydroxy compound. Heating is begun. The reaction mass is heated until it clears, generally at about 100øC. An acid value determination is made to get the "0% reaction value." Next, 0.1%-by-weight esterification catalyst (p-toluene sulfonic acid) is added. The temperature is rapidly raised to 195øC. The acid value is monitored each hour and the % reaction is determined by the reduction in acid value. RESULTS Tables I, II, and III contain the % reaction values for each of the compounds evaluated. These were determined by the % reduction in acid value measured by titration using NaOH (0.5 N). The hydroxyl value was determined on all starting hydroxy compounds, and the equivalent molecular weight was calculated. ACID VALUE The equivalent molecular weight for the stearic acid was determined by acid value. The subsequent acid value determinations were made as the reaction proceeded.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)