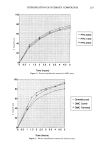
ESTERIFICATION OF HYDROXY COMPOUNDS 253 6O o u 40 2O '-'-' PPG 4000 -+- PPG 1 ooo --,x-- PPG 2000 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 Time (hours) Figure 2. Percent esterification reaction for PPG esters. 100[ 8O 6O 2O --'- Dimethiconol -+- DMC Comb • DMC Terminal 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 Time (hours) Figure 3. Percent esterification reaction for silicone esters.
254 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS reaction temperature for each of the classes studied. Figures 4 and 5 show % reaction at three and four hours respectively. CONCLUSIONS Since it was our desire to study the effect of structural properties on reaction rates rather than determining the rate constants, we chose to maintain as constant the following factors: 1. Temperature: 195 ø C 2. Pressure: atmospheric 3. Catalyst: p-toluene sulfonic acid 4. Catalyst concentration: 0.1% catalyst 5. Mole ratio of reactants: 1.0:1.0 The reaction rates for the preparation of esters can be divided into several classes. These include (a) silicone esters, based upon primary hydroxyl compounds, (b) non-silicone esters made with primary alcohols, and (c) non-silicone esters based upon secondary alcohols. Within each group the principal factor determining esterification rate is the molecular weight of the hydroxy-containing species. Specifically, the higher the equivalent mo- lecular weight of the hydroxy compound being reacted with the stearic acid, the slower the reaction. This relates to the concentration of reactive groups per volume of reaction liquid. Stated another way, the reaction rate is directly proportional to the number of milliequivalents per liter of hydroxyl group present. o 2,000 1,500 1,000 500 "'- Primary OH -+- Silicone OH • Sec OH (PPG) % Reaction Figure 4. Percent esterification reaction in three hours.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)