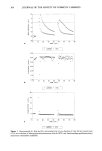
DYNAMIC ELECTROKINETIC AND PERMEABILITY ANALYSIS 115 as reflected by a decrease in the thickness of the conditioning layer. A complete removal of the conditioner residues is not achieved even after two shampooings, as indicated by the value of zeta potential - 12.52 mV, higher than that measured for untreated hair (Figure 7a). Flow rate data also provide evidence for a persistence of a thin layer of the conditioning agent with a thickness of 0.71 Ixm and 0.37 Ixm after the first and second shampooings, respectively. On the other hand, build-up parameters, calculated as a percentage difference between the value of zeta potentials after the second and first treatments for both shampooing and conditioning, suggest that virtually no accumu- lation of the conditioning agents takes place under these experimental conditions (Figure 7a). Figure 7c presents the rate coefficients of desorption of shampoo surfactants, cal- culated from the conductivity data, which indicate a higher desorption rate after the second shampoo application, a result discussed in our previous report (1). CONCLUSIONS Dynamic electrokinetic and permeability analysis was used to investigate various hair conditioner formulations as well as selected raw materials frequently employed in their preparation. The value of zeta potential of treated hair as well as the thickness of deposited layers served as gauges of the effectiveness of the conditioning process. The analyzed products were shown to differ in their ability to modify hair by depositing the conditioning layers varying in thickness from 0.6 to 3.2 Ixm. The zeta potentials were shown to depend on the extent of rinsing, usually decreasing from a relatively high positive value immediately after the treatment to low positive or negative values after 30-minute rinsing with the test solution. REFERENCES (1) J. Jachowicz and C. Williams, Fingerprinting of cosmetic formulations by dynamic electrokinetic and permeability analysis. I. Shampoos, J. Sac. Cosemet. Chem., 45, 309 (1994). (2) G. V. Scott, C. R. Robbins, and J. D. Barnhurst, Sorption of quaternary ammonium surfactants by human hair, J. Sac. Cosmet. Chem., 20, 135 (1969). (3) M. F. Jurczyk, A new quaternary conditioner for damaged hair, Cosmet. Toiletr 106, 91 (1991). (4) P. Finkelstein and K. Laden, The mechanism of conditioning of hair with alkyl quaternary ammonium compounds, Appl. Palym. Symp., 18, 673 (1971). (5) J. Jachowicz, unpublished DEPA results. (6) J. Jachowicz and M. Berthiaume, Heterocoagulation of silicone emulsions on keratin fibers, J. Call. Int. Sci., 133, 188 (1989). (7) C. R. Robbins, G. V. Scott, and J. D. Barnhurst, The influence of presorbed anionic surfactant on the sorption of cationic surfactant by hair, Text. Res. J., 38, 1197 (1968). (8) L. Holt, Cationic-anionic surfactant interaction on wool--Implications for conditioning of human hair, Aust. Sac. Cosmet. Chem., 24th Annual Conference (1989). (9) M. L. Garcia and J. Diaz, Combability measurements on human hair, J. Sac. Cosmet. Chem., 27, 379 (1976). (10) J. Jachowicz, C. Williams, and S. Maxey, Sorption/desorption of ions by dynamic electrokinetic and permeability analysis of fiber plugs, Langmuir, 9, 3085 (1993). (! !) J. Jachowicz and M.D. Berthiaume, Microemulsions versus macroemulsions in hair care products, Cosmet. Toiletr., 108, 65 (!993). (12) I. W. Stapleton, The adsorption of long-chain amines and diamines on keratin fibers, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 34, 285 (!983).
116 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) (18) S. K. Han, Y. K. Kamath, and H.-D. Weigmann, Diffusion of semipermanent dyestuffs in human hair, J. Sac. Cosmet. Chem., 36, I (1985). J. T. Guthrie, A. Kazlauciunas, L. Rongong, and S. Rush, Dyed hair: What is it? Poster presented at the 15th International Federation of Societies of Cosmetic Chemists, London, 1988. J. Jachowicz and M. Berthiaume, unpublished data. G. M. Eccleston and A. T. Florence, Int. J. Cosmet. Sci., 7, 195 (1985). G. M. Eccleston, The structure and rheology of pharmaceutical and cosmetic creams. Cetrimide creams: The influence of alcohol chain length and homolog composition, J. Call. Int. Sci., 57, 66 (1976). B. W. Barry and G. M. Saunders, Kinetics of structure build-up in self bodied emulsions stabilized by mixed emulsifiers, J. Call. Inc. Sci., 41, 331 (1972).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)