CMC STRUCTURE IN HAIR CUTICLE 15
0.020
�
0.015
rJJ
X
,.-.__0.010
rJJ
0.005
0
0 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20
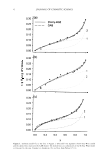
Figure 3. One-dimensional equatorial profile extracted from SAXS pattern, obtained as shown in Figure 2.
We estimated the thickness of the 13- and a-layers from the one-dimensional equatorial profile according
to the method of Ohta et al. (7), using the following formula: l(S) x S4 =a x {cos[TI x S x (13 +o)}}2 x
{sin(TI x S x l3)} 2 ,where S is reciprocal spacing [=(2/A)sin(20/2)} and I is intensity.
with methanol, acetone, and chloroform/methanol, and did not significantly change
with hexane.
The relationships between the CMC structure and extent of hair dyeing are shown in
Figure 5. The average values for the extent of hair dyeing (�E) with each of the
treatments shown in Figure 1 were plotted with the average values of thickness of the
�- and o-layers shown in Figure 4. There was a significant correlation between the extent
of hair dyeing and the thickness of the o-layer, whereas no correlation was seen between
the extent of hair dyeing and the thickness of the �-layer.
DISCUSSION
Using a micro beam X-ray method, we observed the CMC structure without the prestain-
ing or slicing of hair fibers under typical ambient conditions (30°C, 50% relative humidity).
We considered that the present SAXS technique was able to obtain information regard-
ing hair structure under natural conditions, as the hair samples did not require prestain-
ing. Structurai changes in rhe cmicle CMC weie found to be Giuscd by extraction .vith
the various solvents, which seemed to reflect their hydrophobicity. Methanol, which has
0.020
�
0.015
rJJ
X
,.-.__0.010
rJJ
0.005
0
0 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20
Figure 3. One-dimensional equatorial profile extracted from SAXS pattern, obtained as shown in Figure 2.
We estimated the thickness of the 13- and a-layers from the one-dimensional equatorial profile according
to the method of Ohta et al. (7), using the following formula: l(S) x S4 =a x {cos[TI x S x (13 +o)}}2 x
{sin(TI x S x l3)} 2 ,where S is reciprocal spacing [=(2/A)sin(20/2)} and I is intensity.
with methanol, acetone, and chloroform/methanol, and did not significantly change
with hexane.
The relationships between the CMC structure and extent of hair dyeing are shown in
Figure 5. The average values for the extent of hair dyeing (�E) with each of the
treatments shown in Figure 1 were plotted with the average values of thickness of the
�- and o-layers shown in Figure 4. There was a significant correlation between the extent
of hair dyeing and the thickness of the o-layer, whereas no correlation was seen between
the extent of hair dyeing and the thickness of the �-layer.
DISCUSSION
Using a micro beam X-ray method, we observed the CMC structure without the prestain-
ing or slicing of hair fibers under typical ambient conditions (30°C, 50% relative humidity).
We considered that the present SAXS technique was able to obtain information regard-
ing hair structure under natural conditions, as the hair samples did not require prestain-
ing. Structurai changes in rhe cmicle CMC weie found to be Giuscd by extraction .vith
the various solvents, which seemed to reflect their hydrophobicity. Methanol, which has