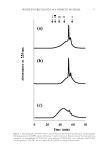
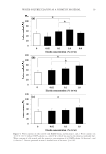
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 122 Figure 5. Sensory profi le for emulsions with PPDO- or PEG-based emulsifi ers. [A = polypropanediol-4/ polyglycerine-3 copolymer sesquistearate (1.5 wt%) and propanediol stearate (3.5 wt%). B = PEG-100 stea- rate and glycerin monostearate blend (5 wt%). C = Steareth-20 (1.5 wt%) and steareth-2 (3.5 wt%). D = PEG-8 stearate (1.5 wt%) and PEG-8 distearate(3.5 wt%).] Formulation 3. Moisturization Ingredients Formulation A (%) Formulation B (%) DI water 81.45 81.45 Disodium EDTA 0.05 0.05 Xanthan Gum 0.25 0.25 Lipovol MOS-70 8.00 8.00 Lipocol SC (cetearyl alcohol) 1.50 1.50 Polypropanediol-4/polyglycerin-3 copolymer sesquistearate 3.50 PPDO-4 stearate 1.50 Lipomulse 165 emulsifi er 5.00 Preservative 0.75 0.75 100.00 100.00 PEG–based emulsifi ers (Formulation 3, Figure 6). A Dermalab Cortex instrument was used to measure the baseline conductance of each panelist’s skin initially before any lotion was applied. Then each lotion was applied to the inner forearm of the panelists only once and conductance readings were taken after 30 min, 1 h, 2 h, 3 h and 4 h. The lotion con- taining PDO-based emulsifi ers showed immediate moisturization that was 47% higher than baseline after 30 min and 57% higher than baseline after 1 h. The lotion containing the PDO-based emulsifi ers showed higher moisturization (statistically signifi cant), at each conductance reading over the 4-h period, than the lotion formulated with the PEG- based emulsifi er.
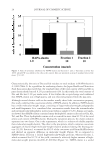
RENEWABLE PDO AND PETROLEUM-DERIVED ALKYLENE OXIDES 123 Figure 6. Moisturization change from baseline (in percent). Longer term moisturization evaluations were performed using a total of 12 female sub- jects selected to participate in the evaluation of two moisturizing creams containing both the PDO-based and petroleum PEG-based emulsifi er. Test material was applied twice a day for 3 days. Moisturization and subject self-assessment of product performance was evaluated 8 and 24 h after last application. Equal moisturization performance was seen between emulsions made with PDO- and petroleum PEG-based emulsifi ers. There was a preference for emulsions with PDO-based emulsifi ers in the subject’s self-assessment evaluation. (Clinical moisturization and self-assessment studies done at Clinical Research Laboratories, LLC/Piscataway, NJ.) (Figure 7). FORMULATIONS Examples of a variety of emulsions made with renewable PDO-based emulsifi ers (body lotion with elegant feel, soft moisturizing cream, and rich/smooth body butter) with a range of viscosities and feel on the skin are given in Formulation 4. CONCLUSION Structure/property comparisons were made of renewable PDO-based versus petroleum- based alkylene oxide feedstocks along with their respective polyethers, emulsifi ers, and cosmetic formulations based on these feedstocks. Based on the structure/property com- parisons, the renewable PDO-based chemistry offers advantages over the petroleum-based EO or PO monomers by being renewable, less reactive/can be handled at ambient pres- sures, nonhazardous/safer chemistry for transporting feedstocks by truck/train and in the manufacturing of cosmetic ingredients, PEG free (no residual EO, no residual 1,4-dioxane), Figure 7. Self-assessment.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)