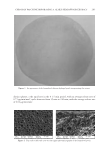
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 256 which is most susceptible to comedones and acne and uses the test material in an expected manner. A positive and negative control is not required because each subject serves as its own control. Statistical analysis compares pretreatment baseline lesion counts with post- treatment lesion counts. REFERENCES (1) A. M. Kligman and O. H. Mills, Acne cosmetic, Arch. Dermatol., 106, 893–897 (1972). (2) A. M. Kligman and T. Kwong, An improved rabbit ear model for assessing comedogenic substances, Br. J. Dermatol., 100, 699–702 (1979). (3) W. E. Morris and S. C. Kwan, Use of the rabbit ear model in evaluating the comedogenic potential of cosmetic ingredients, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 34, 215–225 (1983). (4) J. E. Fulton, Comedogenicity and irritancy of commonly used ingredients in skin care products, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 40, 321–333 (1989). (5) J.E. Fulton Jr, S. R. Pay, and J. E. Fulton 3rd, Comedogenicity of current therapeutic products, cosmet- ics, and ingredients in the rabbit ear, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 10, 96–105 (1984). (6) O. H. Mills and A. M. Kligman, Human model for assessing comedogenic substances, Arch. Dermatol., 118, 903–905 (1982). (7) P. G. Engasser, A. M. Kligman, P. Lazar, J. J. Leyden, P. E. Pochi, A. R. Shalita, and J. S. Strauss, Consensus statement. American Academy of Dermatology Invitational Symposium on Comedogenicity. J. Amer. Acad. Dermatol., 20, 272–277 (1989). (8) Z. D. Draelos and J. C. DiNardo, A re-evaluation of the comedogenicity concept, J. Am. Acad. Dermatol., 54, 507–512 (2006).
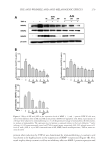
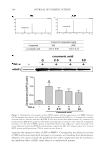
J. Cosmet. Sci., 68, 257–269 ( July/August 2017) 257 Formulation of chitosan patch incorporating Artocarpus altilis heartwood extract for improving hyperpigmentation JUTATIP KWANKAEW, PREEYAWASS PHIMNUAN, SOMBAT WANAUPPATHAMKUL, and JARUPA VIYOCH Department of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Center of Excellence for Innovation in Chemistry, Naresuan University, Phitsanulok, 65000 Thailand (J.K., P.P., J.V.), and International Laboratories Corp. Ltd., Sadhupradist Road, Chongnonsi, Yannawa, Bangkok, 10120 Thailand (S.W.) Accepted for publication June 24, 2017. Synopsis Artocarpus altilis heartwood extract contains the bioactive compound artocarpin which exhibits melanogenesis inhibitory activity. However, the extract has poor solubility which affects the skin permeability of the compound. A chitosan hydrogel patch incorporating A. altilis heartwood extract was formulated to enhance the delivery of an amount of artocarpin suffi cient for depigmenting the skin. The extract was prepared as an o/w microemulsion before blending with an aqueous solution of chitosan. The hydrogel patch was formulated by blending in a 1:1 ratio by weight of 4% w/w chitosan solution and 0.04% w/w extract microemulsion which provides optimal values of the mechanical properties of the patch. The release of artocarpin from the formulated patch (artocarpin content, 0.07 mg/cm2) exhibited two phases the rapid rate (0–15 min) averaged 0.73 μg/min/mm2, and the slow rate (15–240 min) averaged 0.02 μg/min/mm2. The formulated patches signifi cantly improved the hyperpigmented area of the subjects after 3 weeks of application. No adverse events were observed. The results indicate that the formulated chitosan hydrogel patch delivers an effective amount of incorporated artocarpin depigmenting action. INTRODUCTION Artocarpus altilis belongs to the Moraceae family. This evergreen tree, called Sa-Kae in Thai, is found throughout the tropical areas of Southeast Asia and has long been used in traditional folk medicines. Several studies have shown that A. altilis heartwood extract contains phenolic compounds with the ability to inhibit the activity of tyrosinase (1–3), a key enzyme for melanin synthesis. Recent studies have identifi ed artocarpin as a major compound in A. altilis heartwood extract (4–8). The artocarpin in the extract decreases melanin production of B16F1 melanocytes (4,5) and exhibits skin depigmenting effects on the ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced hyperpigmented dorsal skin of C57BL/6 mice (4). Address all correspondence to Jarupa Viyoch at jarupav@nu.ac.th, jarupaviyoch4@yahoo.com.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)