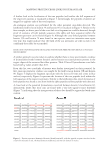
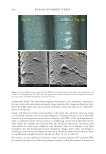
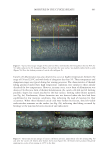
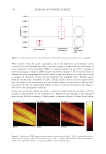
Figure 5. Mass spectrometric characterization of intermolecule lysinoalanine cross-links found between keratin 33B and keratin 80 within a tryptic digest of hair shaft- extracted proteins. 664 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
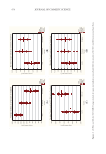
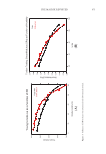
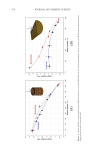
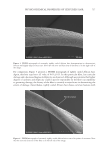
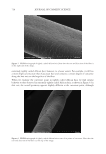
665 MAPPING PROTEIN CROSS-LINKS IN HUMAN HAIR unfold proteins to enable enzymatic digestion and mass spectrometric analysis (10). This proof-of-concept study focused on lanthionine and lysinoalanine cross-links induced by environmental wear and tear. To ensure that the target cross-links were present in our samples, amino acid analysis against lanthionine and lysinoalanine standards measured the absolute quantity of cross-links present in hairs and protein extracts. Although amino acid analysis did not indicate the molecular location of target cross-links, it was essential to creating a robust mass spectrometry and analysis method. In this work, mass spectrometric data acquisition and further analysis of the hair protein extracts did offer additional insights about the approach we developed for mapping cross-links: Figure 6. Protein sequences (human) of keratin 33B and keratin 80, with the peptide sequence involved in the cross-link indicated in red. Figure 7. Mass spectrometric characterization of intermolecule lysinoalanine cross-links found between keratin 34 and keratin 82 within a tryptic digest of hair shaft-extracted proteins. The signal-to-noise level of this cross-link is very low, and interpretation of the data should be done with caution as hardly any difference between the target ions and background ions is seen.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)