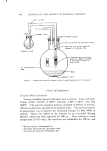
EMULSION STABILITY 399 best in the Triton series, whereas P04 and P•0• were the best in the Pluronic series. The Atlas surfactants were limited to M20, i.e., G-2079. A series of tetradecane-water emulsions was prepared with these surfactants by the spraying method previously detailed using 2 cm of Hg pressure with nitrogen. Atlas G-2079 could not be used in the prepara- tive method. Igepal CO-610 and Pluronic P-94 were the best choices. They (10, 15, and 20% O/W, v/v, lr•o surfactant) passed through an 0.8-v filter pore size and 3-v filter pore size, respectively, and had a total creaming time of 8-12 hours. The emulsions prepared with the discarded surfactants creamed in less than an hour and the minimum filter pore sizes were larger. The emulsions with these chosen surfactants were centrifuged in the Beckman Model E Ultracentrifuge* at 2809, 5227, 9945, 29,500, and 50,740 rpm at 20øC. Creaming studies were possible with both sur- factants at low rates of speed. Free oil was not observed for 5,000 sec at 29,500 rpm but started at 2,500 sec at 40,740 rpm. Ultracentrifugal studies of the rates of free oil formation at 40,740 rpm were then con- ducted for 10, 15, and 20•o emulsions for both surfactants as functions of time. The initial rates of oil separation were 2 x 10-a% oil sep- arated per unit time for all emulsions. Since Igepal CO-610 is a liquid and produced a finer emulsion with tetradecane then the paste Pluronic P:}4, it was considered to be the surfactant of choice in the tetradecane- water system. The cmc value for Igepal-GO-610 is 17 x 10 -4 g/100 ml from surface tension measurements on the Du Nouy Tensiometer.* Analytical Methods Assay of Toluene in Toluene-G-2151-Water Emulsions Approximately 40-50 mg of a 40-50•o emulsion was accurately weighed into a tared 100-ml flask containing approximately 10-20 ml of 95% ethanol. The flask was brought to volrune with 95% ethanol and the solution absorbance was determined against an ethanol blank in the Cary Model 15 Spectrophotometer. The peak absorbances at 268 and 262 mt• were used to determine the concentration, C, from A2•s: (2.619 1./g)C and A•: (2.907 1./g)C. Beer's law holds in the presence and absence of G-2151 surfactant. Beckman Instruments Inc., Spinco Division, Palo Alto, Calif. E. H. Sargent and Co., Kensington, Md.
400 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Determination of Surj•actant G-2151 in Toluene-G-2151-Water Emulsions G-2151 in Water Phase--Replicate samples of the emulsion were placed in two 30-ram, 4 ø sector cells and centrifuged at 1,967 rpm in the Beckman Model E Analytical Ultracentrifuge for the minimum time sufficient to allow complete clearing of the dispersed phase (ca. 500 sec for an emulsion with 1% G-2151 and 50% toluene). The cells were placed backwards in the rotor so that the water phase sediments towards the filling plug. After centrifugation, the water phase was carehfily removed with a syringe equipped with a short needle (so that cream can- not be penetrated) and 0.1 cc of water phase from each cell was placed in a 5-ml volumetric flask. Sufficient I?KI stock solution was added so that the concentration of I,and KI in the final solution was 1 x 10-4M in each and the flask was brought to volume with water. Within 5 rain the ab- sorbance of the solution as a function of Zm• was determined in the Cary Model 15 Spectrophotometer. The concentration, C, of (¾2151 was de- termined from A•.• -- Ag40 = (2.57 x 10 -g) C or from Aa00 -- A,a ---- (4.75 x 10 -4) C, where the wavelengths were chosen such that the ab- sorbances of I,-- I- in the absence of suffactant were equal for a given pair i.e., 303 = '•340 A300 = A275 and where C is in rag/100 mi. The details of this sensitive assay will be published elsewhere. G-2151 in Total Emulsion--The theoretical maximum surfactant concentration possible in the total emulsion is the concentration of G-2151 in toluene surfactant solution multiplied by the amount (ff tolu- ene available for spraying on to the water phase divided by the volume of emulsion. In the preparative procedure utilized, all the ( -2151 was added in the toluene. The theoretical minimum is the concentration of G-2151 in the toluene surfactant solution multiplied by the amount of toluene found by assay in emulsion divided by the volume of emulsion. In the preparative procedure utilized, some of the toluene sprayed on the water was lost due to vaporization and in the apparatus. Thus, the amount found in the emulsion was not the same as the amount added. Approximately 5 g of emulsion was weighed into a 50-ml flask and about 40 cc of water was added. The mixture was shaken to extract surfactant into the water phase and then allowed to stand at either atmospheric pressure or under vacuum until no perceptible trace of
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)