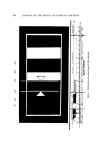
•]•HERMOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF HAIR • •-WEIGHT TRAY FLOAT SUSPENSION COUPLING -- • • PROBE SAMPLE N••FURNAE 361 Figure 1. Schemalic of thermomechanical analyzer. (Printed with permission of the Wil- liams & Wilkins Co.) Imm 4mm PROBE / "-..... •A M PLE TUBE WHEN SAMPLE CONTRACTS PENETRATION EXPANSION EXTENSI ON Figure 2. Thcrmomechanical analysis probe configurations. (Printed with permission of the Williams 8c Wilkins Co.) furnace. The system was heated at a constant rate and probe displace- ment monitored with a linear variable differential transformer which provides a continuous •aphical recording of the probe's movement. The maximran sensitivity of the system is such that a probe displacement of 1.25 • will cause a full-scale pen deflection (10 in.). Differential thermal analysis (DTA) was conducted with a thermal analyzer* incorporating Model 900, Du Pont Co., Instrument Dept., Wilmington, Del. 19898.
362 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS the DCS module. A Perkin-Elmer Model TGS-1 was used for the ther- mogravimetry (TG). The hair samples were obtained from male and female volunteers of various age groups and used without alteration (e.g., degreasing). Chemical Procedures All chemical alterations were performed at room temperature unless otherwise stated. The chemicals were of reagent grade quality and the treated hair was allowed to equilibrate at room conditions (25øC, 30% RH) for at least 24 hours prior to examination. Oxidation Hydrogen peroxide bleaching solutions (6%) were prepared by dilu- tion of a stock 3070 H202solution. The resulting solution was then ad- justed to pH 10 with NH4OH. Performic acid solution was prepared by treating 88% HCOOH with 3070 H202 at a 9-to-1 ratio. Crosslinking Samples were exposed to formaldehyde vapors from a 3670 solution at room temperature. Reduction Samples were reduced with 0.1M thioglycolic acid or benzyl mercap- tan at pH 6.3. Some samples were blocked with a buffered iodoacetate solution. Supercon traction Samples were heated to 95øC in 8M LiBr for 1 hour. Solvents Hair samples were soaked in various organic solvents for 24 hours and then allowed to dry at room conditions. RESULTS AND •)ISCUSSION Viscoelasticity Thermally induced modulus changes which occur in the transverse direction of the hair fiber were measured by applying a weighted probe onto the surface of a hair of known diameter and heating at a pro- grammed rate. Any sudden decrease in the modulus (softening) of the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)