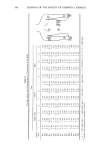
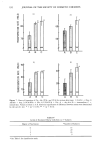
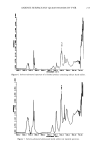
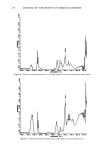
192 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 80 7O l) 6O 50 2) 3) A B C 40 30 4) Figure 7. Rates of formation of Cit, Ala, PCA, and UCA for various skin types. 1) Cit/Cit + Orn 2) Ala/Ala + Asp 3) PCA/PCA + Glu 4) UCA/UCA + His. A -- dry skin B = intermediate C = normal skin. Values are mean _-4- S.E. Statistical significance of differences between means were determined by the use oft test. * = (p 0.05) ** = (p 0.01). Table IV Levels of Nucleated Horny Cells Seen in 77 Subjects Degree of Nucleation *Number of Subjects 0 15 1 29 2 24 3 9 * See Table I for classification scale.
AMINO ACID METABOLITES IN DRY SKIN 193 Table V Levels of Nucleated Horny Cells for Each Skin Type in 77 Subjects Degree of Nucleation* Skin Type A B C 1 2 3 4 5 3 4 2 3 0 0 2 2 10 11 1 0 1 1 4 17 6 1 0 1 1 8 3 2 * See Table I classification scale. metabolism related to keratinization varied in the hyperkeratotic epidermis as shown in Figure 5. Regarding the four compounds mentioned above, His, Glu, Asp, and Orn increased, while their respective metabolites such as UCA, PCA, Ala, and Cit de- creased, suggesting that all the conversions were suppressed when keratinization was pathologically accelerated. The metabolic behavior of each amino acid during a hyper- keratotic period was evaluated in terms of the rate of conversion (Cit/Cit q- Orn, PCA/ PCA q- Glu, Ala/Ala q- Asp, and UCA/UCA q- His). The results are shown in Figure 6. Regarding Cit, which is formed from Arg via Orn, the rate of conversion from Orn to Cit was employed because of the higher value of the correlation coefficient. The rate of conversion for each metabolic pathway was considerably lowered in association with Table VI Amino Acid Metabolism In Vivo METABOLITE METABOLIC PATHWAY PCA • i• :•'l'fi':•'• '- ¾-glutamyI-AA ¾-glutamyl synthetase cyclotrans•erase UCA i'fii'õ'i /NH, : ........... =- :UCA! histidase carbamoyl Orn , ....... ! •,Urea phosphat_,..•½_ Pi Cit --i'b•:•i -- • ' ......
!Arg. ' : ........ ornithine ........ arginase carbamoyltransferase COz Ala / aspartate 4-decarboxylase , ,
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)