ANALYSIS OF NITROSAMINES 295 0 •H 3 HOCH2CH 2 2 CF 3 - C - N - Si(CH3) 3 + NNO -- HOCH2CH2 / (CH3)3SiOCH2CH2 O NNO + 2 CF3CNHCH 3 (CH3)3SiOCH2CH 2 / (16) Table IX Summary of HPLC Methods for Nitrosamine Analysis Method (detection limit) Sample type References HPLC-TEA a (1 to 50 ppb) HPLC-MS b (1 to 5 ppb) HPLC-UV/Vis c (1 to 200 ppb) HPLC-PD a (ppb range) HPLC-PCD e (0.3 to 75 ppb) HPLC-EC f HPLC-FD g (ppb range) Foodstuffs Air Water Physiological specimens Tobacco products Rubber products Automobiles Leather products Industrial chemicals Cutting fluids Cosmetics & raw materials Blood collection tubes Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Air Water Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Cutting fluids Cosmetics & raw materials Miscellaneous Physiological specimens Metal-working fluids Cosmetics & raw materials Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Water Ethanolamines Miscellaneous Foodstuffs Miscellaneous Water Miscellaneous 115, 161, 192, 219, 220, 221, 224, 234 101 91 141 129, 179, 181 215, 307 67 69 136 111 1, 16, 42, 43, 48-54, 57, 62, 108 40 47, 196, 199 127 101 91 198 115 111 34, 55, 56, 60, 61, 74, 99, 137, 274, 306 140, 142, 182, 245 80, 141, 204 64 96, 275 73, 170 189 193 63 146 289 97, 291 193 207, 288 TEA, Thermal energy analyzer. MS, Mass spectrometer. UV/Vis, Ultraviolet/visible detection. PD, Polarographic detection. PCD, Photoconductivity detection. EC, Electrochemical detection. FD, Fluorescence detection.
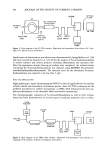
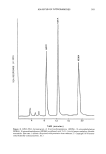
296 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS GC CARRIER GAS INJECTION HE ATED PTFE TUBE PORT 250øC TEA CATALYTIC PYROLYZER OZONE -80øC -150øC COLD TRAPS I VACUUM PUMP OPTICAL FILTER PM TUBE Figure 2. Flow diagram of the GC-TEA interface. (Reprinted with permission from reference 84. Copy- right 1975 Elsevier Science Publishers.) Applications of derivatization procedures were demonstrated by Spiegelhalder et al. (28) and more recently by Sommer et al. (29,30) for the analysis of N-nitrosodiethanolamine in several cosmetic and toiletry products including alkanolamine raw materials (30). After the appropriate sample clean-up procedures were completed, the isolated residue containing the N-nitrosodiethanolamine was silylated using MSHFBA (N-methyl-N- trimethylsilylheptafluorobutyramide). The detection limit for the derivatized N-nitroso- diethanolamine was reported to be less than 5 ppb. HPLC-TEA APPLICATIONS High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) is directly applicable for the analysis of both volatile and nonvolatile nitrosamine species. Since GC-TEA techniques are the preferred procedures for volatile nitrosamines, so HPLC-TEA techniques have been ap- plied predominantly to the thermally labile nonvolatile nitrosamines. The chromatographic separation of N-nitrosodiethanolamine as well as other nitrosa- mines has been demonstrated on several types of packing materials such as silica, LIQUID INJECTION POnT ••r• CARnlERF..r'{ILTFOZOtlETEA•ICATALYTICPYnOLIZ[RHEAIoeOGAS .Pt_c COLUMN øfiOeC - 150'C COLD TRAPS Figure 3. Flow diagram of the HPLCoTEA interface. (Reprinted with permission from reference 27. Copyright 1978 Cosmetic, Toiletry and Fragrance Association.)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)