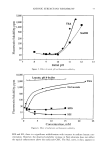
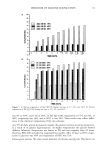
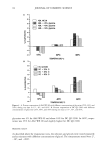
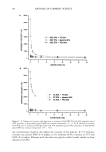
SURFACTANTS AND BLOOD CLEANSING BY SLS SOLUTIONS 109 100 J 50- 40- 30 0.00 I I I 0.01 0.02 0.03 % SLS ß l:)cuf•L-"P• 0 DI Wfdnr m DIW•l Figure 6. Sodium chloride-based douche/CPC1 solutions. the surfactant is salted out of solution. Decyl glucoside is a nonionic surfactant that does not ionize in the solution, but like SLS and CPC1, it is able to compete with the blood cells for the water molecules once micelies have formed. The micelles formed by decyl glucoside are able to attract water because of the polar glucose groups on the molecules. Decyl glucoside in deionized water (darkened square, Figure 7) is able to cleanse 76% of the blood, an amount almost identical to that of the 74% cleansed by aleionized water alone. In the lower concentrations (below 0.09%), the cleansing accomplished by these solutions is by the sodium chloride in solution. The cleansing decreases over the next two concentrations (0.11% and 0.15%) because the decyl glucoside is able to lyse the cells before the sodium chloride can remove them from the cloth, and the denatured cellular material is then only partially cleansed (Figures 7, 8). As the decyl glucoside increases, the cleansing rises over the next three concentrations (0.175%, 0.20%, and 0.30%)
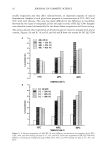
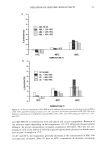
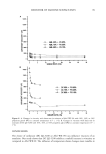
110 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 90 80- 50- •0 m •0 I I I I I 0.00 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 % Dec'• Glucoslde O DI Wmlim' Figure 7. 0.9% NaC1/decyl glucoside solutions. (Figures 7, 8). At the lowest and highest concentrations, the decyl glucoside does not inhibit the blood cleansing, but in fact, it seems that it and sodium chloride are an effective team in cleansing the blood. In the douche solution (Figure 9), the cleansing does decrease slightly, but the reduction is not as drastic as seen in the other sodium chloride solutions. Since decyl glucoside is a nonionic surfactant, the pH of the acidic douche solution does not affect its cleansing ability. CONCLUSIONS Overall, the blood cleansing ability of the surfactants is inferior to that of the sodium chloride solutions. Sodium chloride removes the blood by lifting the entire cell from the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)