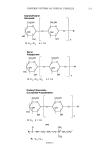
256 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE a triethylamine catalyst. The used AKD was synthesized from a mixture of acyl chlo- rides, the main carbon chain of which comprised 16 and 18 atoms in the ratio of 3:7. Both protic solvent and aprotic solvent showed good results. As a protic solvent, ethanol was used. When the ethanol was added again as a solvent in the further purification step, the final product could be easily crystallized from the reaction medium. Two crystalli- zations resulted in pure PC-9 s product. In the case of toluene as an aprotic solvent, the final products showed a red-brown color when the reaction temperature was too high, and protic solvent such as ethanol needed to be added to purify the crude product. The characteristic features of PC-9 s are the following: two alkyl groups, one amide bond, one hydroxyl group, and one ketone group at lB-position. The reaction scheme and the structure of the PC-9 s were represented in Figure 1. The synthesis of new pseudoceramide was carried out via a one-step reaction. Thus, it is a very simple and effective process to prepare pseudoceramides. NMR and the FT-IR spectra confirmed the structure of the PC-9 s. These results are typically characteristic of ketene dimers in reaction with an amine and an alcohol. The FT-IR spectrum showed the typical amide peak, where an ester bond was not formed. This can be explained by the relative reactivity of amine and alcohol with AKD (18), since it is known that the amine group is much more reactive than the hydroxyl group with the AKD. In support of this, it has been reported that the reaction between alcohol and AKD was very sluggish without a catalyst. INTERMOLECULAR HYDROGEN BONDING AMONG PC-9Ss The barrier function of ceramides is due to the lameliar structure formation with fatty acid and cholesterol. It was known that the intermolecular hydrogen bonding among head groups of the ceramides plays an important role in the formation of a stable lameliar structure (19). In the crystalline state, the carbonyl group within the amide bond takes q- Nt-I2CH2CH2OH .-N3ICH2CH2OH o Figure 1. Reaction scheme of PC-9 s (R• = RoCH2).
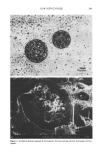
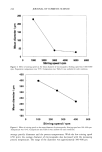
SYNTHESIS OF PC-9 s 257 part in hydrogen bonding with the hydroxyl group of another molecule. However, it was observed that when the pseudoceramide, PC-9 s was dissolved in a hydrophobic solvent such as chloroform (a liquid state), hydrogen bonding among the molecules weakened greatly or completely disappeared. The FT-IR spectra of PC-9 s in a solid state (KBr) and a liquid state (chloroform) was used to determine the existence of intermolecular hy- drogen bonds. The reaction of AKD and 2-aminoethanol resulted in the ring-opening reaction of IB-lactone and the new bond formation of a IB-keto group (1717.13 cm-•) and an amide bond (1649.15 cm -•) shown in the KBr pellet, where the hydroxyl group of its head group shows a hydrogen bond with the amide bond. With PC-9 s dissolved in chloroform (a liquid state), it was observed that the wave number of the amide bond was shifted into the higher wave number (1662.72 cm-•), which meant that the intermo- lecular hydrogen bonds disappeared in the chloroform, which was certified by the wave number shifting of the amide bond (A u = 13.57 cm -•) (Figure 2). This demonstrates that there is an intermolecular hydrogen bond among molecules, which plays an im- portant role in lameliar structure formation. Besides the intermolecular hydrogen bond- ing, there is the strong possibility to also form intramolecular hydrogen bonds. It was reported that an intramolecular hydrogen bond occurred in the six-member ring very easily (20). As a theoretical drawing, Figure 3 illustrates an intramolecular hydrogen bonding of PC-9 s. PHASE DIAGRAM OF THE LIPID MIXTURE AND ITS OBSERVATION Figure 4 shows the phase diagram of a PC-9S/stearic acid/cholesterol complex system and a typically characteristic cross-polarized picture at a point within the phase diagram. The P½.•(KBr) PC-9={CHCI3) 170•-• t6E 2.72 L leto 1600 Figure 2. FT-IR spectrum of PC-9 s in the crystal state (KBr) and liquid state (chloroform).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)