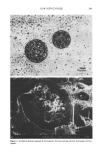
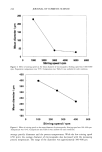
SYNTHESIS OF PC-9 s 261 125 1 20 •' 115 • 11o .- lO5 -- rr 100 95 90 Tb Ta 1 H 3H 5H Time --+--MLE •Control 1 +Control 2 Tb: Before treatment of organic solvent T•: One hour after organic solvent treatment 1H: After one hour from the emulsion treatment 3H ß After 3 hours from the emulsion treatment 5H: After 5 hours from the emulsion treatment Figure 6. Fast restoration function of the multilamellar emulsion on damaged skin. multilamellar emulsion using PC-9 s with that of controls (regular emulsions) by mea- suring the decrease in TEWL. When the multilamellar emulsion using PC-9 s was applied to damaged skin, it was shown that restoration from water loss with the multilamellar emulsion treatment was significantly faster than with the controls. The fast restoration function of PC-9 s can be applied to the special dermatological prepara- tion for sensitive skin or atopic skin. CONCLUSION The reaction of AKD and alcoholic amine provided an effective synthetic pathway for a new pseudoceramide, PC-9 s. Its high purity and yield enable an industrial application. The carbonyl group of amide bond can form the intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bond with the hydroxyl group, which was demonstrated by the wave number shifting in FT-IR spectra. According to cross-polarized microscopy measurement, it was determined that PC-9 s had high intrinsic characteristics to form a lameliar structure with fatty acid and cholesterol. It was also demonstrated, by observing the optical
262 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE anisotropy of "Maltese crosses" by use of a cross-polarized microscope, that the pseudo- stratum corneum components had an intrinsic power with emulsifiers and oils to form a multilamellar emulsion. It was also demonstrated by TEWL measurement that the multilamellar emulsion has a water barrier function on the damaged skin. In the future, the effect of the multilamellar emulsion on an atopic, dry, scaly, and sensitive skin will be investigated in cosmetic formulations. (6) (7) (8) (9) (lO) (11) (12) (13) (14) (15) (16) (17) (18) (19) (20) (21) REFERENCES (1) P. Wertz, D. Downing, R. Freinkel, and T. Trazyk, d. Invest. Dermatol., 83, 193-195 (1984). (2) P.M. Elias, Arch. Dermatol. Res., 270, 95-117 (1981). (3) H.J. Yardley, Int. d. Cosmet. Sci., 9, 13-19 (1987). (4) D. Maes, K. Marenus, and W. P. Smith, Cosmet. Toiletr., 105, 43-50 (1990). (5) M. Kerscher et al., Eur. d. Dermatol., 1, 39-43 (1991). G. Imokawa, S. Akasaki, A. Kawamata, S. Yano, and T. Takaishi,d. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 40, 273-285 (1989). E. A. Hannon and R. M. Bell, Duke University, WO patent 92-03129 (1992). G. Rousset, Laboratories Inocosm, WO patent 92-21321 (1992). J. Casey, P. Cheerham, P. Harries, D. Hyliands, J. T. Mitchell, and A. V. Rawlings, Unilever PLC, WO patent 94-10131 (1994). H. Lambers, F. Farin, W. Keuning, and W. Vander Wilden, 2nd ASCS, 106-125 (1995). S. Yano, A. Kawamata, Y. Minematsu, S. Akazaki, M. Zama, G. Imokawa, N. Takaishi, T. Ohtomo, and T. Higashi, Kao Co., EP patent 0282816 (1988). P. Critchley, S. Kirsch, A. V. Rawlings, and I. Scott, Unilever PLC, WO patent 92-06674 (1992). P. Critchley, S. Kirsch, A. V. Rawlings, and I. Scott, Unilever PLC, WO patent 92-06982 (1992). Y. Ohashi, M. Suda, S. Yano, A. Kawamata, M. Okuda, and G. Imokawa, Kao Co., USpatent 5221757 (1993). T. Suzuki, J. Fukasawa, H. Iwai, I. Sugai, O. Yamashita, and A. Kawamata, 17th IFSCC, International Congress Yokohama, Vol. 1, A10! (1992). M. Foldvari, University of Saskatchewan, WO patent 95-03 787. P. W. Wertz and D. T. Downing,J. LipidRes., 24, 759-765 (1983). R. E. Kirk and D. F. Othmer, Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology (Interscience, New York, 1952), Vol. 8, pp. 110-111. H. Iwai, J. Fukasawa, M. Fukuda, I. Sugai, H. Uchida, and T. Suzuki, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. Jpn., 30, 310 (1996). J. March, Advanced Organic Chemistry--Reactions, Mechanisms, and Structure, 4th ed. (John Wiley & Sons, New York, 1992). G. Dahms, Cosmet. Toiletr., 101, 113-115 (1986).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)