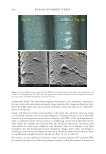
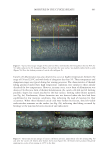
637 THE ROLE OF THE SCALP MICROBIOME IN HEALTH AND DISEASE DANDRUFF Now that we understand Malassezia and fungi, this paper will now discuss dandruff. Dandruff is big business—making the skincare industry a lot of money. The market associated with skin microbiology is estimated at more than $20 billion USD per year, with $5 billion of that being anti-dandruff shampoo alone. This makes dandruff a significant problem that accounts for a large percentage of dermatologist visits and a health care burden. As so many research publications focus on the gut and bacteria, skin eukaryotes are poorly understood. This is an exploitable knowledge gap and, hopefully, we can learn to exploit skin mycology to drive business and improve human health. Dandruff represents a less severe version of seborrheic dermatitis, but both are the result of a similar aetiology (12). Dandruff consists of scalp flaking and pruritis (itch). Seborrheic dermatitis also includes visible irritation and may extend beyond the scalp to the eyebrows, nasal labial fold, and beard. But dandruff is more than flaking and itch. The stratum corneum is completely disrupted, mixed up, and disorganized and completely unable to perform its function, which is to protect us from what is outside and to keep our water in (13). To understand what causes dandruff, it is useful to initially review historic treatment paradigms. Historically, the most effective materials used to treat dandruff had one commonality: antifungal efficacy. This may lead us to hypothesize that fungi are involved in dandruff genesis. As the scalp microbiome is dominated by Malassezia, it would also make sense that Malassezia that might be important in causing dandruff. The problem here is that Malassezia are found on a healthy scalp as well as one with dandruff. Many hours and dollars have been sacrificed investigating the cause of dandruff to enable better treatment design. Initially, when it was discovered in 1994 that Malassezia consisted of multiple species, we were convinced we would be able to identify a causative species and thereby target the right Malassezia (14). We executed a parallel group clinical study and compared dandruff sufferers with an inherent scalp flaking score (ASFS) of greater than 24 to normal subjects with an inherent scalp flaking score of less than 10. Unfortunately, the two groups were the same, and everyone had the same scalp microbiome (15). If this is correct, and it remains so even today, how can Malassezia be the cause of dandruff? MALASSEZIA AND THEIR ROLE ON SKIN COMMENSALISM There are multiple types of microbe–host relationship terms: commensalism, in which one partner benefits but the other is unaffected pathogenicity, in which one benefits and the other is harmed and mutualism, in which both benefit (16). It has been long known that Malassezia inhabit the skin of all humans, with both healthy and diseased skin. In the absence of any other data, the default interpretation would be that Malassezia benefit from living on us, utilizing us as a food source and biological niche with no obvious benefit or harm, leading to definition of the relationship as commensal. Indeed, virtually all the technical literature prior to 2000 would classify Malassezia as commensals on human skin, perhaps occasionally being referred to an “opportunistic pathogen.” Very likely, in some instances, this is a correct assumption. In other cases, we now think it likely that a more complicated relationship exists.
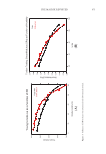
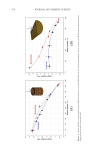
638 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE PATHOGENICITY It is important to dig deeper and understand that Malassezia live on sebum, eating the oils on skin (17). Human sebum is created as sebaceous triglycerides that are secreted from the sebaceous gland. When there are few Malassezia, the skin is covered with mostly triglycerides similar to olive oil, which is good for your skin. When Malassezia are present, they break down the triglycerides that are good for your skin, and they are replaced by irritating free fatty acids. We hypothesized if Malassezia cause dandruff, these fatty acids might reconstitute dandruff. To test this hypothesis, we identified two groups of subjects for a clinical trial, one of dandruff sufferers (ASFS 24) and one of non-dandruff sufferers (ASFS 8). We then removed the Malassezia with antifungal treatment and reduced all the flaking scores to 8 and performed a placebo controlled split scalp application of either oleic acid (the most abundant free fatty acid released from sebum) or its vehicle. The subjects who initially had dandruff begin flaking again at the treatment sites, and those flakes look exactly like human dandruff flakes. This indicates that application of a Malassezia metabolite, oleic acid, is able to induce a dandruff-like desquamation. Interestingly enough, in the subjects who did not initially have dandruff, the non-dandruff population, this no longer works. This divides human race into two groups—those who get dandruff and those who do not (15,17). For now, the individual susceptibility remains unknown. It may be a skin barrier problem in which the fatty acids are able penetrate better. It may be a host response to either the fatty acids or to a Malassezia metabolite that has penetrated through the skin. In any event, it is now clear humans can be divided into those who can get dandruff and those who do not. This is termed individual susceptibility and is common in microbially-mediated disease. The concept of individual susceptibility in microbially-mediated disease also complicates how we design, execute, and interpret clinical trials and disease models. If one compares “diseased” to “normal” subjects seeking a causal microbe, if the disorder is based on an underlying individual susceptibility, it will be impossible to find the microbe. It will be present on both groups, unable to cause disease in the nonsusceptible group. Furthermore, the microbe and its entire pathogenic mechanism may be on the nonsusceptible group, simply unable to cause disease. This indicates we need to seriously consider the implications of clinical investigation into microbially-mediated disease. To elucidate the organism and mechanism, it would be essential to work with diseased individuals in which one can treat the disorder and observe changes in the microbiology and homeostatic mechanisms during treatment and reversion (3,11). This also complicates understanding if a microbe is a pathogen, a commensal, or a mutual. Commensalism means that only one of the organisms benefit in this case, Malassezia eat the sebum and digest us with no other effect. All this goes back to Heinrich Koch, a legend of microbiology because of his “postulates of disease” (18). In order for a microbe to cause a disease, it must be found on diseased, rather than healthy, organisms. You must be able to isolate the microbe, grow it up in pure culture, put it back on the healthy organism and cause the disease, and then reisolate it and show it caused the disease. These postulates worked great in the 19th and early 20th centuries, initiated germ theory, and brought about the modern era of medical research. However, the world has now become more complicated (19). Koch’s postulate that organisms must be found on all organisms with the disease, but not healthy organisms, stumbles on the concept of individual susceptibility. Even Koch himself in the early 19th
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)